Impact Factor
ISSN: 1449-1907
Int J Med Sci 2023; 20(3):385-391. doi:10.7150/ijms.81214 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Liver Injury in Patients with COVID-19: A Retrospective Study
Department of Gastroenterology, The First Affiliated Hospital of Xi'an Jiao Tong University, Xi'an, People's Republic of China
*These authors have contributed equally to this work.
Abstract
Objectives: The objective of this study is to explore the incidence, characteristics, risk factors, and prognosis of liver injury in patients with COVID-19.
Methods: We collected clinical data of 384 cases of COVID-19 and retrospectively analyzed the incidence, characteristics, and risk factors of liver injury of the patients. In addition, we followed the patient two months after discharge.
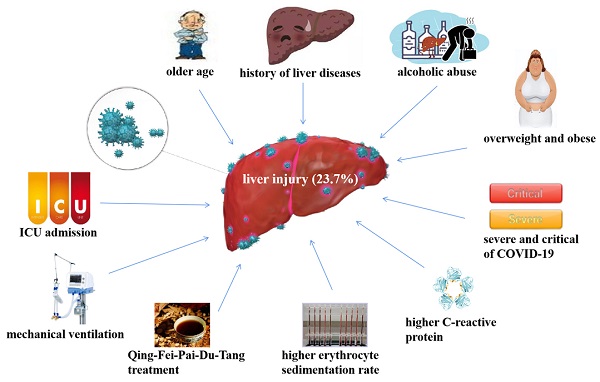
Results: A total of 23.7% of the patients with COVID-19 had liver injury, with higher serum AST (P < 0.001), ALT (P < 0.001), ALP (P = 0.004), GGT (P < 0.001), total bilirubin (P = 0.002), indirect bilirubin (P = 0.025) and direct bilirubin (P < 0.001) than the control group. The median serum AST and ALT of COVID-19 patients with liver injury were mildly elevated. Risk factors of liver injury in COVID-19 patients were age (P = 0.001), history of liver diseases (P = 0.002), alcoholic abuse (P = 0.036), body mass index (P = 0.037), severity of COVID-19 (P < 0.001), C-reactive protein (P < 0.001), erythrocyte sedimentation rate (P < 0.001), Qing-Fei-Pai-Du-Tang treatment (P = 0.032), mechanical ventilation (P < 0.001), and ICU admission (P < 0.001). Most of the patients (92.3%) with liver injury were treated with hepatoprotective drugs. 95.6% of the patients returned to normal liver function tests at 2 months after discharge.
Conclusions: Liver injury was commen in COVID-19 patients with risk factors, most of them have mild elevations in transaminases, and conservative treatment has a good short-term prognosis.
Keywords: COVID-19, liver injury, liver function tests, Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2, Chinese traditional medicine

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact