3.2
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1449-1907
Int J Med Sci 2023; 20(3):292-306. doi:10.7150/ijms.80727 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Cardiovascular and lipid-lowering effects of a marine lipoprotein extract in a high-fat diet-induced obesity mouse model
EuroEspes Biomedical Research Center, Institute of Medical Science and Genomic Medicine, 15165-Bergondo, Corunna, Spain.
Abstract
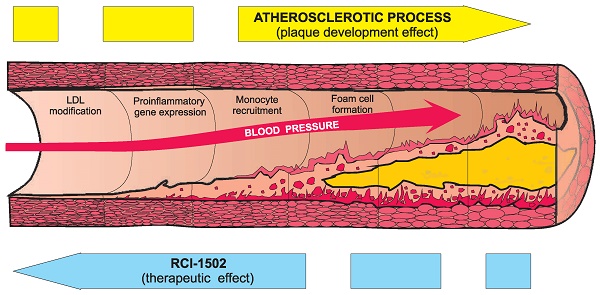
Obesity is a major health challenge worldwide, with implications for diabetes, hypertension and cardiovascular disease (CVD). Regular consumption of dark-meat fish is linked to a lower incidence of CVD and associated metabolic disorders due to the presence of long-chain omega-3 fatty acid ethyl esters in fish oils. The aim of the present study was to determine whether a marine compound like a sardine lipoprotein extract (RCI-1502), regulates fat accumulation in the heart of a high-fat diet-induced (HFD) mouse model of obesity. To investigate its effects in the heart and liver, we conducted a randomized, 12-week placebo-controlled study in which we analyzed the expression of vascular inflammation markers, obesity biochemical patterns and related CVD pathologies. Male HFD-fed mice treated with a RCI-1502-supplemented diet showed reduced body weight, abdominal fat tissue and pericardial fat pad mass density without systemic toxicity. RCI-1502 significantly reduced triacylglyceride, low-density lipoprotein and total-cholesterol concentrations in serum, but increased HDL-cholesterol levels. Our data show that RCI-1502 is beneficial for reducing obesity associated with a long-term HFD, possibly by exerting a protective effect on lipidic homeostasis, indicated also by histopathological analysis. These results collectively indicate that RCI-1502 acts as a cardiovascular therapeutic nutraceutical agent, which modulates fat-induced inflammation and improves metabolic health.
Keywords: Cardioprotective, Obesity, Cardiovascular disease, Marine lipoproteins, Nutraceutical

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact