Impact Factor
ISSN: 1449-1907
Int J Med Sci 2022; 19(3):486-487. doi:10.7150/ijms.71614 This issue Cite
Erratum
PRMT4 promotes hepatocellular carcinoma progression by activating AKT/mTOR signaling and indicates poor prognosis: Erratum
Department of General Surgery, The First Affiliated Hospital of Nanchang University, Nanchang, Jiangxi 330006, China.
Published 2022-3-3
Corrected-article in Int J Med Sci, Volume 18, 3588
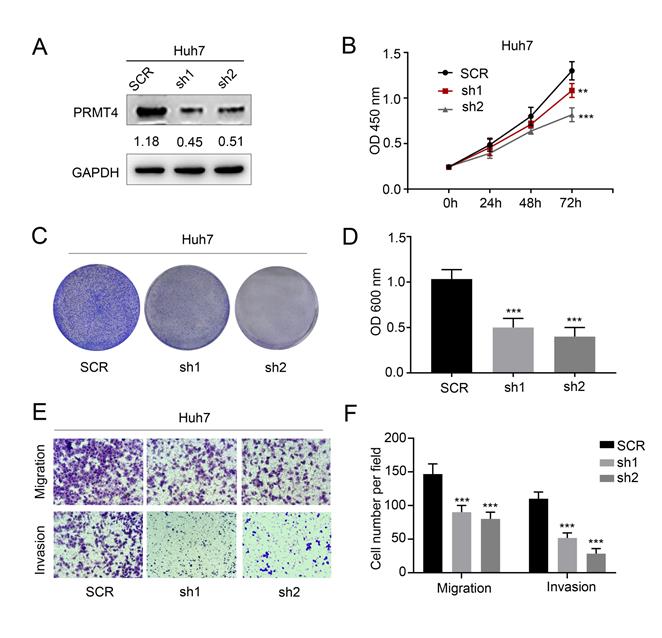
The original version of our article [1] unfortunately contained an error in Figure 3E. The picture of Huh7 cell invasion assay picture in the sh2 group in Figure 3E was incorrectly assembled. We sincerely apologize for this error. All authors were informed and approved the corrected figures. Figure 3 should be corrected as follows
PRMT4 knockdown inhibits proliferation, migration, and invasion of HCC cells in vitro. (A) Western blots showing the downregulation of PRMT4 in Huh7 cells. (B) The effect of PRMT4 knockdown on the proliferation of Huh7 was measured by CCK-8 assays. (C) The effect of PRMT4 knockdown on the proliferation of Huh7 cells was detected by crystal violet assays. (D) The OD value of crystal violet assays in Huh7 cells. (E) The effect of PRMT4 knockdown on the migration and invasion of Huh7 cells was detected by Transwell assays (×400 magnification). (F) Calculation of cells that migrated and invaded through the filter in Huh7 cells. Measurement data were expressed as mean ± SD, and the experiments were repeated at least 3 times. **P< 0.01, ***P < 0.001 vs SCR group. SCR, scrambled; shRNA, short hairpin RNA.
References
1. Du P, Luo K, Li G, Zhu J, Xiao Q, Li Y, Zhang X. PRMT4 promotes hepatocellular carcinoma progression by activating AKT/mTOR signaling and indicates poor prognosis. Int J Med Sci. 2021;18(15):3588-3598 doi:10.7150/ijms.62467
Author contact
![]() Corresponding authors: Xingjian Zhang, Department of General Surgery, The First Affiliated Hospital of Nanchang University, No. 17 Yongwai Zheng Street, Nanchang, Jiangxi 330006, China. E-mail: lfyzhangbocom. Yong Li, Department of General Surgery, The First Affiliated Hospital of Nanchang University, No. 17 Yongwai Zheng Street, Nanchang, Jiangxi 330006, China. E-mail: yzaduncu.edu.cn; Tel: +86-791-8869-2554; Fax: +86-791-8869-2554.
Corresponding authors: Xingjian Zhang, Department of General Surgery, The First Affiliated Hospital of Nanchang University, No. 17 Yongwai Zheng Street, Nanchang, Jiangxi 330006, China. E-mail: lfyzhangbocom. Yong Li, Department of General Surgery, The First Affiliated Hospital of Nanchang University, No. 17 Yongwai Zheng Street, Nanchang, Jiangxi 330006, China. E-mail: yzaduncu.edu.cn; Tel: +86-791-8869-2554; Fax: +86-791-8869-2554.

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact