3.2
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1449-1907
Int J Med Sci 2021; 18(14):3214-3223. doi:10.7150/ijms.60774 This issue Cite
Research Paper
15,16-dihydrotanshinone I inhibits EOMA cells proliferation by interfering in posttranscriptional processing of hypoxia-inducible factor 1
1. Department of Pediatric Surgery, Xinhua Hospital, School of Medicine, Shanghai Jiaotong University, Shanghai, China
2. Division of Pediatric Oncology, Shanghai Institute of Pediatric Research, Shanghai, China
3. Department of Reconstructive Surgery, Xinhua Hospital, School of Medicine, Shanghai Jiaotong University, Shanghai, China
Abstract
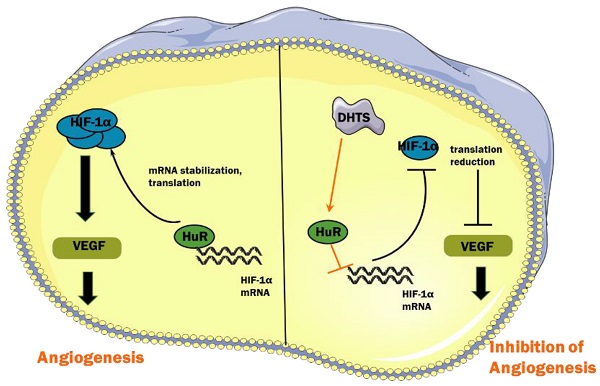
Infantile hemangioma (IH), which threatens the physical and mental health of patients, is the most common benign tumor in infants. Previously, we found that 15,16-dihydrotanshinone I (DHTS) was significantly more effective at inhibiting hemangioma proliferation in vitro and in vivo than the first-line treatment propranolol. To investigate the underlying mechanism of DHTS, we used EOMA cells as a model to study the effect of DHTS. We compared the transcriptomes of control and DHTS-treated EOMA cells. In total, 2462 differentially expressed genes were detected between the groups. Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes pathway analysis revealed downregulated activity of the hypoxia-inducible factor 1 alpha (HIF-1α) signaling pathway in EOMA cells following treatment with DHTS. Thus, we investigated HIF-1α expression at protein and mRNA levels. Our results revealed that DHTS downregulated HIF-1α expression by interfering in its posttranscriptional processing, and the RNA-binding protein HuR participated in this mechanism. Our findings provide a basis for clinical transformation of DHTS and insight into pathogenic mechanisms involved in IH.

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact