3.2
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1449-1907
Int J Med Sci 2023; 20(3):329-345. doi:10.7150/ijms.80358 This issue Cite
Review
Genomic Fingerprint Associated with Familial Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis: A Review
1. Department of Respiratory Medicine, The Second Hospital of Jilin University, Changchun, China.
2. Hospital of Jilin University, Changchun, China.
Abstract
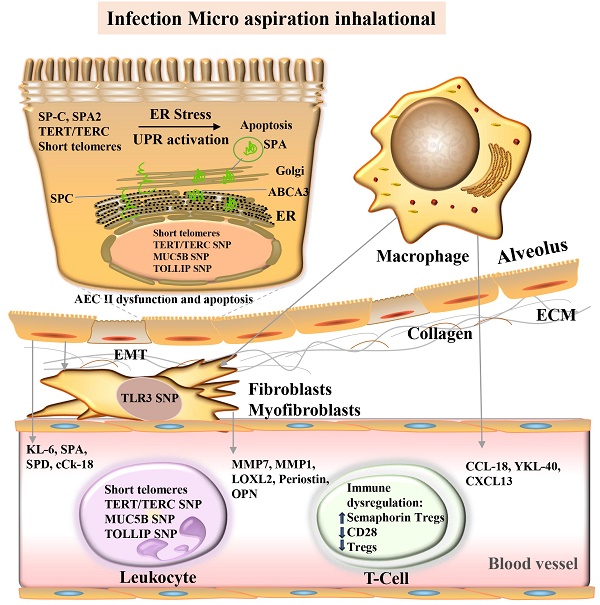
Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF) is a severe interstitial lung disease; although the recent introduction of two anti-fibrosis drugs, pirfenidone and Nidanib, have resulted in a significant reduction in lung function decline, IPF is still not curable. Approximately 2-20% of patients with IPF have a family history of the disease, which is considered the strongest risk factor for idiopathic interstitial pneumonia. However, the genetic predispositions of familial IPF (f-IPF), a particular type of IPF, remain largely unknown. Genetics affect the susceptibility and progression of f-IPF. Genomic markers are increasingly being recognized for their contribution to disease prognosis and drug therapy outcomes. Existing data suggest that genomics may help identify individuals at risk for f-IPF, accurately classify patients, elucidate key pathways involved in disease pathogenesis, and ultimately develop more effective targeted therapies. Since several genetic variants associated with the disease have been found in f-IPF, this review systematically summarizes the latest progress in the gene spectrum of the f-IPF population and the underlying mechanisms of f-IPF. The genetic susceptibility variation related to the disease phenotype is also illustrated. This review aims to improve the understanding of the IPF pathogenesis and facilitate his early detection.
Keywords: Familial idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis, Sporadic idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis, Telomerase-associated gene, Mucin 5B, Surfactant-related gene.

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact