ISSN: 1449-1907International Journal of Medical Sciences
Int J Med Sci 2024; 21(1):27-36. doi:10.7150/ijms.76817 This issue Cite
Review
Novel Insights into Prokineticin 1 Role in Pregnancy-related Diseases
1. Shanghai Changning Maternity & Infant Health Hospital, China.
2. The Department of Obstetrics, Shanghai Obstetrics and Gynecology Hospital of Fudan University, Shanghai 200080, China.
3. NHC Key Lab of Reproduction Regulation (Shanghai Institute of Planned Parenthood Research), Hospital of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Fudan University, Shanghai 200080, China.
4. Shanghai Key Laboratory of Female Reproductive Endocrine Related Diseases, Hospital of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Fudan University, Shanghai 200080, China.
5. Laboratory for Reproductive Immunology, Institute of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Hospital of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Fudan University, Shanghai 200080, China.
Abstract
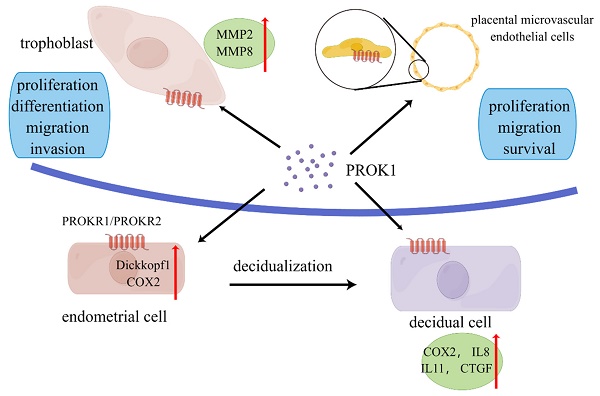
Prokineticin 1 (PROK1) is a secreted protein involved in a range of physiological activities such as cell proliferation, migration, angiogenesis, and neuronal cell proliferation. Emerging evidences show that PROK1/PROK receptors (PROKRs) are expressed by trophoblasts, and decidual stroma cells at the maternal-fetal interface. PROK1 plays a critical role in successful pregnancy establishment by regulating the decidualization, implantation and placental development. Dysregulation of prokineticin signaling has been described in certain pathological states associated with pregnancy, including pre-eclampsia, recurrent miscarriage and fetal growth restriction. In this review, the expression and pleiotropic roles of PROK1 under physiological and pathological pregnancy conditions are discussed.
Keywords: prokineticin1, maternal-fetal interface, angiogenesis, recurrent miscarriage, preeclampsia, fetal growth restriction

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact