3.2
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1449-1907
Int J Med Sci 2023; 20(11):1460-1468. doi:10.7150/ijms.87089 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Dasatinib regulates the proliferation and osteogenic differentiation of PDLSCs through Erk and EID3 signals
1. School and Hospital of Stomatology, Cheeloo College of Medicine, Shandong University, Shandong, China.
2. Shandong Key Laboratory of Oral Tissue Regeneration & Shandong Engineering Laboratory for Dental Materials and Oral Tissue Regeneration, Shandong, China.
3. Shandong Provincial Clinical Research Center for Oral Diseases, Shandong, China.
4. Tianjin Stomatological Hospital, School of Medicine, Nankai University, Tianjin, China & Tianjin Key Laboratory of Oral and Maxillofacial Function Reconstruction, Tianjin, China.
*Co-first authors: These two authors contributed equally to this work and should be considered as co-first authors.
Abstract
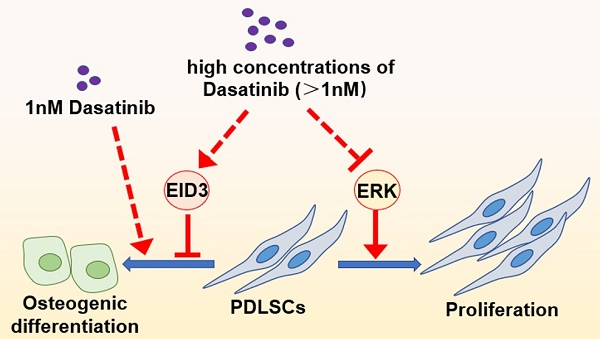
Periodontal ligament stem cells (PDLSCs) are important candidate seed cells for alveolar bone tissue engineering. Dasatinib is a tyrosine kinase inhibitor, and its influence on the osteogenic differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells is a controversial topic. The present study explored the effects of different concentrations of dasatinib on the proliferation and osteogenic differentiation of PDLSCs and tentatively revealed the related mechanism. The results of CCK8 showed that low concentrations of dasatinib (1 nM) did not affect proliferation, while high concentrations of dasatinib significantly inhibited the proliferative activity of PDLSCs. This could be related to the inhibiting effects of dasatinib on Erk signals. ALP staining, alizarin red staining, and western blot proved that low concentrations of dasatinib (1 nM) promoted the osteogenic differentiation of PDLSCs, while high concentrations of dasatinib inhibited it. The negative effects of dasatinib on osteogenic differentiation were reversed when EID3 was knocked down, suggesting that EID3 mediates the regulation of dasatinib on the osteo-differentiation of PDLSCs. Taken together, high concentrations of dasatinib inhibited the proliferation and osteogenic differentiation of PDLSCs through Erk and EID3 signals, while low concentrations of dasatinib could be a potential method to enhance the bone regeneration ability of PDLSCs.
Keywords: periodontal ligament stem cells, dasatinib, Erk, EID3, osteogenic differentiation, proliferation.

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact