3.2
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1449-1907
Int J Med Sci 2023; 20(11):1417-1424. doi:10.7150/ijms.83371 This issue Cite
Research Paper
U-shaped association between triglyceride and risk of incident diabetes in normoglycemic males with NAFLD: A population-base cohort study
1. Department of Endocrinology, The First Affiliated Hospital of Guangxi Medical University, Nanning, Guangxi, China.
2. Transplant Medical Center, The Second Affiliated Hospital of Guangxi Medical University, Nanning, Guangxi 530007, China.
3. Guangxi Key Laboratory of Organ Donation and Transplantation, Nanning, Guangxi 530007, China.
4. Guangxi Transplantation Medicine Research Center of Engineering Technology, Nanning, Guangxi 530007, China.
5. Department of Endocrinology, Bishan Hospital of Chongqing, Bishan, Chongqing, China.
6. Department of Endocrinology and Metabolism, Kyoto Prefectural University of Medicine, 465 Kajii-cho, Kawaramachi-Hirokoji, Kamigyo-ku, Kyoto, Japan.
7. Department of Gastroenterology, Asahi University Hospital, 3-23, Hashimoto-cho, Gifu, Japan.
*Contributed equally
Abstract
Background: Serum triglyceride (TG) was an important biomarker for nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), and the association between TG and incident type 2 diabetes mellitus is still under debate with some studies suggesting that elevated TG increase the risk of incident T2DM while others indicative of a negative relationship. These controversial findings may be partially due to the inclusion of the participants with NAFLD. The association between TG and incident type 2 diabetes mellitus in people with NAFLD remained unclear. Therefore, this study aimed to characterize the relationship between the baseline TG levels and incident type 2 diabetes mellitus in a male Japanese cohort with NAFLD.
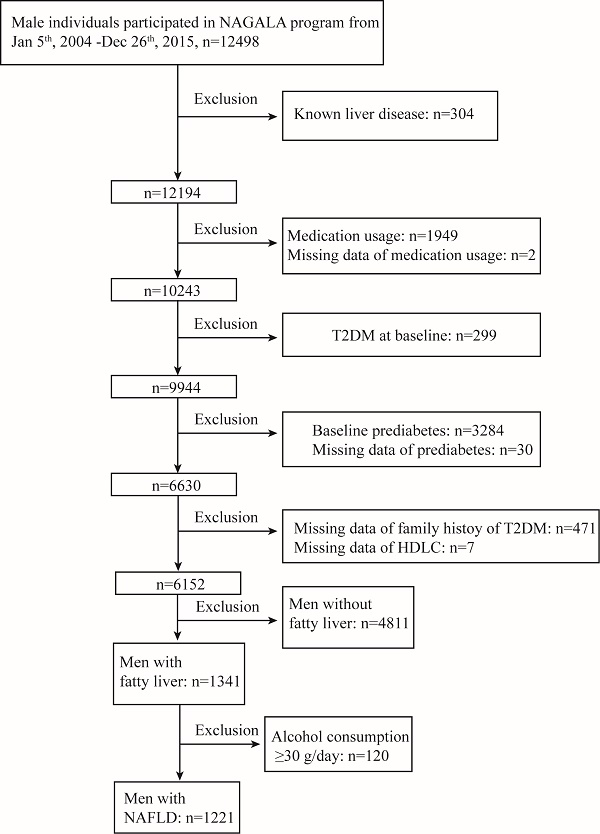
Methods: A total of 1221 males with NAFLD were enrolled from the Nagala (NAFLD in the Gifu Area Longitudinal analysis) study conducted from 2004 to 2015. Cox proportional hazards models were performed to examine the relationship between baseline TG concentration and incident type 2 diabetes mellitus. A two-piecewise linear regression model was explored to evaluate the threshold effect of the baseline TG levels on type 2 diabetes mellitus incidence by using a smoothing function.
Results: During a median follow-up of 6.05 years, 39 males with NAFLD at baseline developed type 2 diabetes mellitus. The risk of incident type 2 diabetes mellitus was significantly associated with baseline TG concentration in males with NAFLD after fully adjustment for confounders, with per 10 mg/dl elevation in TG levels increasing the risk of incident diabetes by 8.5% (HR=1.085, CI=1.039-1.132; P<0.001). However, no typical dose-dependent positive association between type 2 diabetes mellitus incidence and the TG levels was observed across the TG tertiles. Interestingly, a U-shaped association between TG concentration and risk of incident type 2 diabetes mellitus was revealed by the two-piecewise linear regression analysis. Baseline TG concentration lower than the threshold values (TG <53mg/dl) were negatively associated with risk of incident type 2 diabetes mellitus. With each 10mg/dl increase in baseline TG levels, the risk of incident type 2 diabetes mellitus decreased by nearly 59% (HR=0.413, 95% CI=0.220-0.778). In contrast, when TG levels were higher than the threshold values (TG>53mg/dl), the risk of incident diabetes increased 9.1% with every 10mg TG elevation (HR=1.091, 95% CI=1.046-1.137).
Conclusions: A U-shaped relationship was observed between baseline TG levels and incident type 2 diabetes mellitus in a male normoglycemic Japanese population with NAFLD, although extrapolation of the finding to other populations should be made with caution.
Keywords: triglyceride, Incident type 2 diabetes mellitus, U-shaped association, NAFLD

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact