ISSN: 1449-1907
Int J Med Sci 2022; 19(12):1753-1761. doi:10.7150/ijms.73740 This issue Cite
Review
Roles for c-Abl in postoperative neurodegeneration
1. Department of Anesthesiology, Hainan Hospital of Chinese People's Liberation Army General Hospital, Sanya, China.
2. Department of Cardiology, Hainan Hospital of Chinese People's Liberation Army General Hospital, Sanya, China.
3. Department of Geriatric Cardiology, Chinese People's Liberation Army General Hospital, Beijing, China.
4. Center for the Study of Aging and Human Development and Geriatrics Division, Medical School of Duke University, North Carolina, USA.
5. Center for Healthy Aging and Development Studies, National School of Development, Peking University, Beijing, China.
6. Department of Anesthesiology, The Third Medical Center of Chinese People's Liberation Army General Hospital, Beijing, China.
7. Central Laboratory, Hainan Hospital of Chinese People's Liberation Army General Hospital, Sanya, China.
*Co-first authors.
Abstract
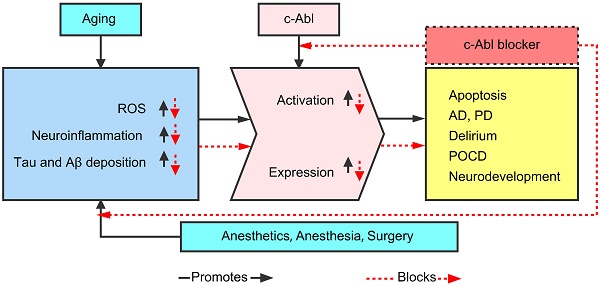
The nonreceptor tyrosine kinase c-Abl is inactive under normal conditions. Upon activation, c-Abl regulates signaling pathways related to cytoskeletal reorganization. It plays a vital role in modulating cell protrusion, cell migration, morphogenesis, adhesion, endocytosis and phagocytosis. A large number of studies have also found that abnormally activated c-Abl plays an important role in a variety of pathologies, including various inflammatory diseases and neurodegenerative diseases. c-Abl also plays a crucial role in neurodevelopment and neurodegenerative diseases, mainly through mechanisms such as neuroinflammation, oxidative stress (OS), and Tau protein phosphorylation. Inhibiting expression or activity of this kinase has certain neuroprotective and anti-inflammatory effects and can also improve cognition and behavior. Blockers of this kinase may have good preventive and treatment effects on neurodegenerative diseases. Cognitive dysfunction after anesthesia is also closely related to the abovementioned mechanisms. We infer that alterations in the expression and activity of c-Abl may underlie postoperative cognitive dysfunction (POCD). This article summarizes the current understanding and research progress on the mechanisms by which c-Abl may be related to postoperative neurodegeneration.
Keywords: Alzheimer's disease, Nonreceptor tyrosine kinase, Oxidative stress, Parkinson's disease, Postoperative cognitive dysfunction, Postoperative neurodegeneration

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact