3.2
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1449-1907
Int J Med Sci 2022; 19(3):490-498. doi:10.7150/ijms.69400 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Deep Learning-based Artificial Intelligence Improves Accuracy of Error-prone Lung Nodules
1. Division of Pulmonary Medicine, Taipei Tzu Chi Hospital, Buddhist Tzu Chi Medical Foundation, New Taipei City, Taiwan.
2. School of Medicine, Tzu Chi University, Hualien, Taiwan.
3. Division of thoracic surgery, Taipei Tzu Chi Hospital, Buddhist Tzu Chi Medical Foundation, New Taipei City, Taiwan.
4. Department of Medical Imaging, Taipei TzuChi General Hospital, Buddhist Tzu Chi Medical Foundation, New Taipei City, Taiwan.
5. Department of ASUS Intelligent Cloud Services (AICS), ASUSTek Computer Inc.
6. Department of Chinese Medicine, Taipei Tzu Chi Hospital, Buddhist Tzu Chi Medical Foundation.
7. School of Post-Baccalaureate Chinese Medicine, Tzu Chi University, Hualien, Taiwan.
8. Department of Research, Taipei Tzu Chi Hospital, Buddhist Tzu Chi Medical Foundation, New Taipei City, Taiwan.
9. Department of Research, Taipei Tzu Chi Hospital, Buddhist Tzu Chi Medical Foundation, New Taipei City, Taiwan.
Abstract
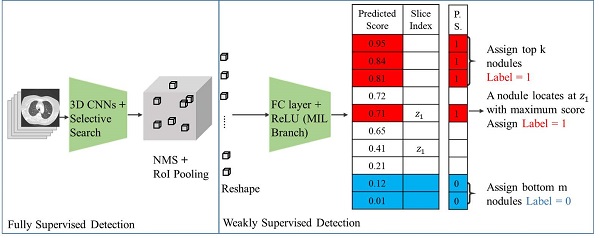
Introduction: Early detection of lung cancer is one way to improve outcomes. Improving the detection of nodules on chest CT scans is important. Previous artificial intelligence (AI) modules show rapid advantages, which improves the performance of detecting lung nodules in some datasets. However, they have a high false-positive (FP) rate. Its effectiveness in clinical practice has not yet been fully proven. We aimed to use AI assistance in CT scans to decrease FP.
Materials and methods: CT images of 60 patients were obtained. Five senior doctors who were blinded to these cases participated in this study for the detection of lung nodules. Two doctors performed manual detection and labeling of lung nodules without AI assistance. Another three doctors used AI assistance to detect and label lung nodules before manual interpretation. The AI program is based on a deep learning framework.
Results: In total, 266 nodules were identified. For doctors without AI assistance, the FP was 0.617-0.650/scan and the sensitivity was 59.2-67.0%. For doctors with AI assistance, the FP was 0.067 to 0.2/scan and the sensitivity was 59.2-77.3% This AI-assisted program significantly reduced FP. The error-prone characteristics of lung nodules were central locations, ground-glass appearances, and small sizes. The AI-assisted program improved the detection of error-prone nodules.
Conclusions: Detection of lung nodules is important for lung cancer treatment. When facing a large number of CT scans, error-prone nodules are a great challenge for doctors. The AI-assisted program improved the performance of detecting lung nodules, especially for error-prone nodules.
Keywords: artificial intelligence, lung nodules, CT images

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact