3.2
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1449-1907
Int J Med Sci 2021; 18(14):3090-3096. doi:10.7150/ijms.60776 This issue Cite
Research Paper
BRD4 inhibition promotes TRAIL-induced apoptosis by suppressing the transcriptional activity of NF-κB in NSCLC
1. Department of Radiation and Medical Oncology, Zhongnan Hospital of Wuhan University, Wuhan, China.
2. Hubei Key Laboratory of Tumor Biological Behaviors, Zhongnan Hospital of Wuhan University, Wuhan, China.
3. Hubei Clinical Cancer Study Center, Zhongnan Hospital of Wuhan University, Wuhan, China.
#These authors contributed equally to this work.
Abstract
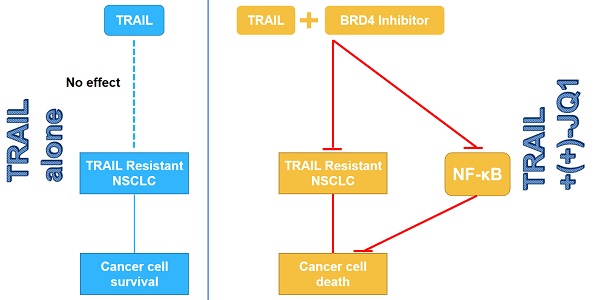
Tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis inducing ligand (TRAIL) and agonistic antibodies against TRAIL death receptors (DR) can induce apoptosis preferentially in tumor cells while causing virtually no damage to normal cells. However, their therapeutic potential is limited by occurring resistance in tumor cells, including non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). Thus, elucidation of the molecular targets and signaling pathways responsible for TRAIL resistance is imperative for devising effective therapeutic strategies for TRAIL resistant cancers. In the present study, we demonstrated that inhibition of Bromodomain-containing protein 4 (BRD4) or genetic knock-down of BRD4, an epigenetic reader and master transcription coactivator, can sensitize lung cancer cells to TRAIL. This sensitization is in a caspase-dependent manner. Inhibition of BRD4 by small molecule inhibitor (+)-JQ-1 and genetic knock-down of BRD4 can both recruit the FADD and activate caspases. The sensitization did not regulate the death receptors DR4 and DR5. Moreover, BRD4 inhibition can block TRAIL-induced IKK activation by suppressing the transcriptional activity of NF-κB. These findings indicate that targeting combination therapy with TRAIL and BRD4 inhibitors can be a promising strategy to overcome TRAIL resistance in NSCLC.

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact