3.2
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1449-1907
Int J Med Sci 2021; 18(14):3059-3065. doi:10.7150/ijms.61153 This issue Cite
Review
The role and mechanisms of Microglia in Neuromyelitis Optica Spectrum Disorders
1. Department of Pharmacy, The Second Xiangya Hospital, Central South University, Changsha, 410011, Hunan, China.
2. Institute of Clinical Pharmacy, Central South University, Changsha, 410011, Hunan, China.
3. Department of Ophthalmology, The Second Xiangya Hospital, Central South University, Changsha, Hunan 410011, China.
4. Hunan Clinical Research Center of Ophthalmic Disease, Changsha, Hunan 410011, China.
Abstract
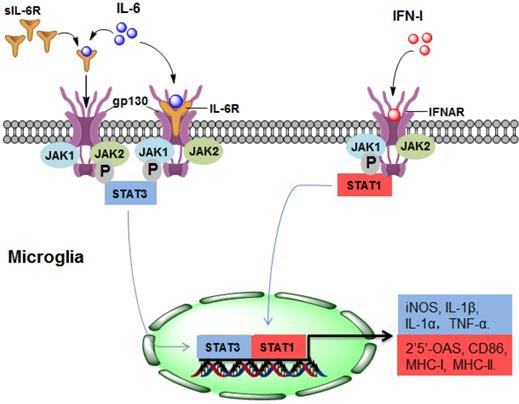
Neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorder (NMOSD) is an autoimmune neurological disease that can cause blindness and disability. As the major mediators in the central nervous system, microglia plays key roles in immunological regulation in neuroinflammatory diseases, including NMOSD. Microglia can be activated by interleukin (IL)-6 and type I interferons (IFN-Is) during NMOSD, leading to signal transducer and activator of transcription (STAT) activation. Moreover, complement C3a secreted from activated astrocytes may induce the secretion of complement C1q, inflammatory cytokines and progranulin (PGRN) by microglia, facilitating injury to microglia, neurons, astrocytes and oligodendrocytes in an autocrine or paracrine manner. These processes involving activated microglia ultimately promote the pathological course of NMOSD. In this review, recent research progress on the roles of microglia in NMOSD pathogenesis is summarized, and the mechanisms of microglial activation and microglial-mediated inflammation, and the potential research prospects associated with microglial activation are also discussed.
Keywords: microglia, neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorder, demyelination, microglial activation

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact