3.2
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1449-1907
Int J Med Sci 2021; 18(8):1866-1876. doi:10.7150/ijms.53685 This issue Cite
Research Paper
A network pharmacology based approach for predicting active ingredients and potential mechanism of Lianhuaqingwen capsule in treating COVID-19
1. School of Basic Medicine, Chengdu University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Chengdu, China.
2. Academic Department, Zhuhai Ebang Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd. Zhuhai, China.
#These authors contributed equally to this work.
Abstract
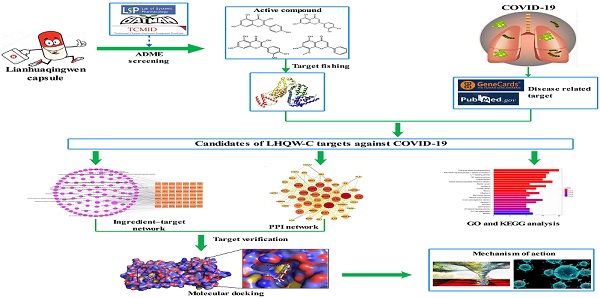
The outbreak of severe respiratory disease caused by SARS-CoV-2 has led to millions of infections and raised global health concerns. Lianhuaqingwen capsule (LHQW-C), a traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) formula widely used for respiratory diseases, shows therapeutic efficacy in the application of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19). However, the active ingredients, drug targets, and the therapeutic mechanisms of LHQW-C in treating COVID-19 are poorly understood. In this study, an integrating network pharmacology approach including pharmacokinetic screening, target prediction (targets of the host and targets from the SARS-CoV-2), network analysis, GO enrichment analysis, KEGG pathway enrichment analysis, and virtual docking were conducted. Finally, 158 active ingredients in LHQW-C were screen out, and 49 targets were predicted. GO function analysis revealed that these targets were associated with inflammatory response, oxidative stress reaction, and other biological processes. KEGG enrichment analysis indicated that the targets of LHQW-C were highly enriched to several immune response-related and inflammation-related pathways, including the IL-17 signaling pathway, TNF signaling pathway, NF-kappa B signaling pathway, and Th17 cell differentiation. Moreover, four key components (quercetin, luteolin, wogonin, and kaempferol) showed a high binding affinity with SARS-CoV-2 3-chymotrypsin-like protease (3CL pro). The study indicates that some anti-inflammatory ingredients in LHQW-C probably modulate the inflammatory response in severely ill patients with COVID-19.
Keywords: Lianhuaqingwen capsule, COVID-19, 3CL pro, SARS-CoV-2, network pharmacology

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact