ISSN: 1449-1907
Int J Med Sci 2024; 21(8):1552-1558. doi:10.7150/ijms.95736 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Comparison emergence of sedation, using dexmedetomidine and remimazolam, in spinal anaesthesia - double blinded randomized controlled trial
1. Department of Anesthesiology and Pain medicine, Konkuk University Medical Center, Konkuk University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
2. Department of Infection and Immunology, Konkuk University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
3. Department of Medicine, Institute of Biomedical Science and Technology, Konkuk University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
4. Department of Medical Education, Konkuk University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
Abstract
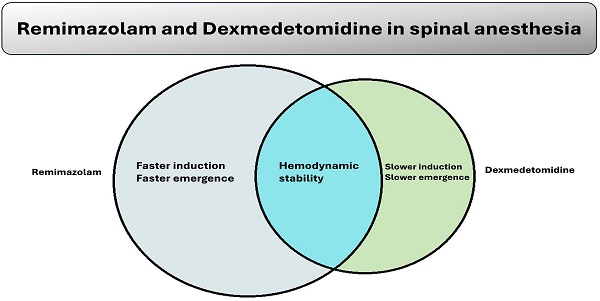
Background: Continuous intravenous infusion of remimazolam may be suitable for sedation in patients undergoing regional anaesthesia. However, there have been no studies comparing remimazolam and dexmedetomidine for this purpose. This study compared emergence from sedation between dexmedetomidine and remimazolam following continuous intravenous infusion in patients undergoing spinal anaesthesia.
Methods: This double-blinded, randomised controlled trial assessed the sedative effects of dexmedetomidine and remimazolam. Following spinal anaesthesia, patients were sedated using continuous intravenous infusion of either dexmedetomidine (D group) or remimazolam (R group).The D group received dexmedetomidine administered at 6 mL/kg/h (6 µg/kg/h) for 10 minutes, followed by 1 mL/kg/h (1 µg/kg/h). The R group received remimazolam administered at 6 mL/kg/h (6 mg/kg/h) for 10 minutes, followed by 1 mL/kg/h (1 mg/kg/h). Sedation levels were evaluated using the Modified Observer's Assessment of Alertness/Sedation (MOAA/S) scale. The time to reach MOAA/S ≤ 3 from the start of drug infusion and the time to reach MOAA/S = 5 from the end of infusion were recorded. Hemodynamic parameters and respiratory rate were also monitored.
Results: The R group reached MOAA/S ≤ 3 significantly faster than the D group during induction of sedation (4 ± 1 minutes and 11 ± 3 minutes, respectively, p < 0.001). The R group also reached MOAA/S = 5 significantly faster than the D group during emergence from sedation (11 ± 3 minutes and 16 ± 5 minutes, respectively, p < 0.001). Both groups maintained stable hemodynamic parameters and respiratory rate without any significant differences, although the mean heart rate was significantly lower in the D group than in the R group after the start of infusion.
Conclusion: Remimazolam demonstrated significantly faster induction of and emergence from sedation compared to dexmedetomidine, with no significant differences in haemodynamics or respiratory depression.
Keywords: Sedation, Dexmedetomidine, Remimazolam, Spinal anesthesia, Hemodynamics, Respiratory rate

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact