ISSN: 1449-1907
Int J Med Sci 2024; 21(3):547-561. doi:10.7150/ijms.90484 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Dual-specificity phosphatase 1 interacts with prohibitin 2 to improve mitochondrial quality control against type-3 cardiorenal syndrome
1. Xiyuan Hospital, China Academy of Chinese Medical Sciences, Beijing, China.
2. Graduate School, Beijing University of Chinese Medicine, Beijing, China.
3. Cardiovascular department, Guang'anmen Hospital, China Academy of Chinese Medical Sciences, Beijing, 100053, China.
4. Kunming Municipal Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Yunnan, China.
*The first two authors contributed equally to this article.
Abstract
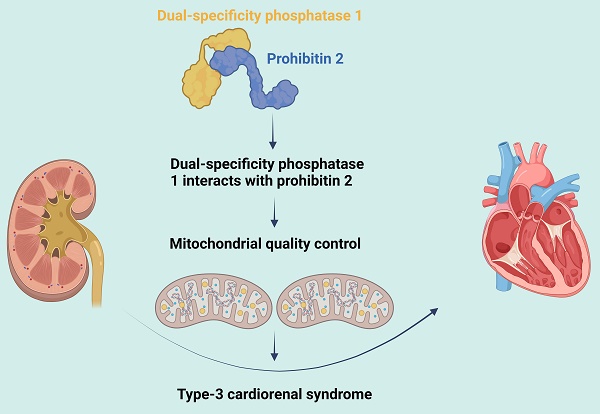
Type-3 cardiorenal syndrome (CRS-3) is acute kidney injury followed by cardiac injury/dysfunction. Mitochondrial injury may impair myocardial function during CRS-3. Since dual-specificity phosphatase 1 (DUSP1) and prohibitin 2 (PHB2) both promote cardiac mitochondrial quality control, we assessed whether these proteins were dysregulated during CRS-3-related cardiac depression. We found that DUSP1 was downregulated in heart tissues from a mouse model of CRS-3. DUSP1 transgenic (DUSP1Tg) mice were protected from CRS-3-induced myocardial damage, as evidenced by their improved heart function and myocardial structure. CRS-3 induced the inflammatory response, oxidative stress and mitochondrial dysfunction in wild-type hearts, but not in DUSP1Tg hearts. DUSP1 overexpression normalized cardiac mitochondrial quality control during CRS-3 by suppressing mitochondrial fission, restoring mitochondrial fusion, re-activating mitophagy and augmenting mitochondrial biogenesis. We found that DUSP1 sustained cardiac mitochondrial quality control by binding directly to PHB2 and maintaining PHB2 phosphorylation, while CRS-3 disrupted this physiological interaction. Transgenic knock-in mice carrying the Phb2S91D variant were less susceptible to cardiac depression upon CRS-3, due to a reduced inflammatory response, suppressed oxidative stress and improved mitochondrial quality control in their heart tissues. Thus, CRS-3-induced myocardial dysfunction can be attributed to reduced DUSP1 expression and disrupted DUSP1/PHB2 binding, leading to defective cardiac mitochondrial quality control.
Keywords: CRS-3, DUSP1, PHB2, mitochondrial quality control

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact