3.2
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1449-1907
Int J Med Sci 2024; 21(2):219-233. doi:10.7150/ijms.86210 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Integrative Analysis of N6-methyladenosine RNA modifications related genes and their Influences on Immunoreaction or fibrosis in myocardial infarction
1. Department of Cardiology, Shanghai Chest Hospital, Shanghai Jiao Tong University School of Medicine, Shanghai 200030, China.
2. Laboratory of Oral Microbiota and Systemic Diseases, Shanghai Ninth People's Hospital, College of Stomatology, Shanghai Jiao Tong University School of Medicine, Shanghai 200125, China.
3. National Center for Stomatology; National Clinical Research Center for Oral Diseases; Shanghai Key Laboratory of Stomatology, Shanghai 200011, China.
4. Department of Oral Surgery, Shanghai Ninth People's Hospital, Shanghai Jiao Tong University School of Medicine, Shanghai 200011, China.
5. Department of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine, Shanghai Ninth People's Hospital, Shanghai Jiao Tong University School of Medicine, Shanghai 200011, China.
†These authors contributed equally to this work and share first authorship.
Abstract
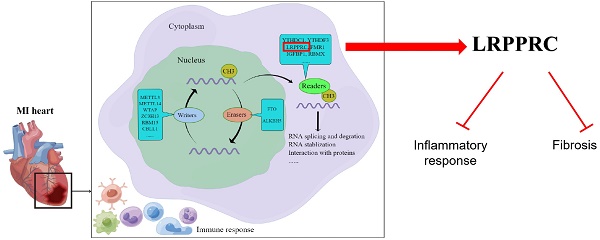
Increasing studies have shown that N6-methyladenosine (m6A) modification plays an important role in cardiovascular diseases. In this study, we systematically investigated the regulatory mode of m6A genes in myocardial infarction (MI) by combining bioinformatics analysis of clinical samples with animal experiments. We utilized gene expression data of clinical samples from public databases to examine the expression of m6A genes in heart tissues and found a large difference between the healthy control group and MI group. Subsequently, we established an MI diagnosis model based on the differentially expressed m6A genes using the random forest method. Next, unsupervised clustering method was used to classify all MI samples into two clusters, and the differences in immune infiltration and gene expression between different clusters were compared. We found LRPPRC to be the predominant gene in m6A clustering, and it was negatively correlated with immunoreaction. Through GO enrichment analysis, we found that most differentially expressed genes between the two clusters were profibrotic. By means of WGCNA, we inferred that GJA4 might be a core molecule in the m6A regulatory network of MI. This study demonstrates that m6A regulators probably affects the immune-inflammatory response and fibrosis to regulate the process of MI, which provides a potential therapeutic target.
Keywords: MI, m6A regulation, immune response, fibrosis, LRPPRC, WGCNA

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact