3.2
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1449-1907
Int J Med Sci 2024; 21(1):169-174. doi:10.7150/ijms.87752 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Nutritional index in relation to prognosis of endometrial cancer
1. Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, St. Vincent's Hospital, College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Seoul, Republic of Korea.
2. Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Eunpyeong St. Mary's Hospital, College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Seoul, Republic of Korea.
Abstract
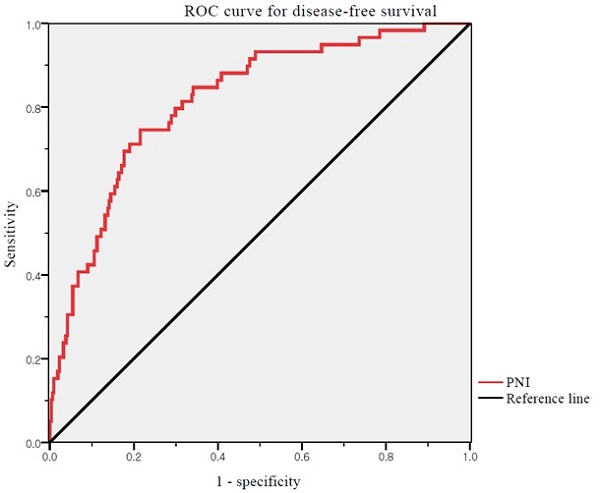
Objective: Evaluate the prognostic value of the prognostic nutritional index (PNI) in patients with endometrial cancer (EC).
Method: Laboratory and clinicopathological data from 370 patients who were diagnosed with EC between January 2010 and December 2021 were reviewed. The PNI was analyzed for correlations with recurrence and survival. The receiver operating characteristic curves were generated for the PNI. Optimal cut-off values were determined as the points at which the Youden index (sensitivity + specificity - 1) was maximal. Based on the results of the ROC curve analysis, the patients were grouped into high and low PNI groups. Differences in the clinicopathological characteristics between patients with high and low PNI were compared between the two groups. The effects of the prognostic factors were analyzed using univariate and multivariate Cox proportional hazards model.
Results: The optimal cutoff value of the PNI was 52.74 for DFS (area under the curve: 0.817; 95% CI: 0.738-0.858, p <0.001). Significantly more patients in the low PNI group experienced recurrence (30.6% vs. 5.2%, p <0.001) and cancer-related death (17.8% vs. 2.8%, p <0.001). In multivariate analysis, PNI were independent prognostic factors for both DFS and overall survival OS.
Conclusion: Low PNI was significantly associated with worse clinical outcomes in patients with EC. Our findings demonstrate that the PNI may be clinically reliable and useful as a prognostic marker for patients with EC. Further large-scale prospective studies are needed to confirm our findings.
Keywords: endometrial cancer, uterine cancer, prognostic factors, prognostic nutritional index, PNI

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact