3.2
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1449-1907
Int J Med Sci 2023; 20(12):1584-1591. doi:10.7150/ijms.85430 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Uric acid-based ratios for predicting renal failure in Chinese IgA nephropathy patients
Division of Nephrology, Department of Medicine, West China Hospital, Sichuan University, Chengdu, Sichuan, China.
Abstract
Objective: The uric acid/albumin ratio (UAR), a novel, simple, and compositive laboratory biomarker, has recently attracted attention for predicting disease prediction and disease prognosis. However, whether uric acid-related biomarkers (especially UAR) could serve as prognostic indicator for IgAN is unclear.
Methods: In this retrospective cohort study, biopsy-confirmed IgAN patients from 2009 to 2017 from West China Hospital were evaluated. The optimal cutoff value of UAR for renal outcome was defined using the Youden index by the area under receiver operating characteristic curve (AUC). The patients were then categorized into the high UAR group and the low UAR group. Renal endpoints were defined as progression to ESRD, eGFR decreased ≥50% of the baseline level, or initiation of renal replacement treatment. Kaplan‒Meier survival analysis and Cox regression analysis were used to identify factors influencing IgAN outcomes.
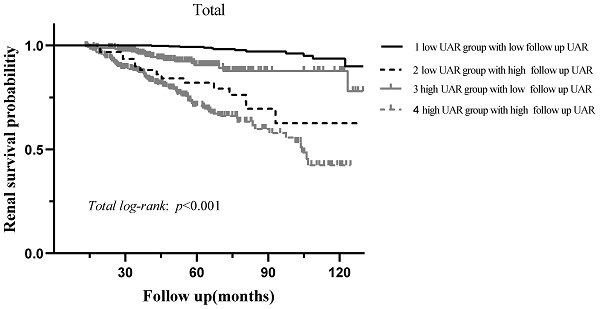
Results: A total of 1143 patients with a median age of 33.0 (26.0-42.0) (44.2% men) were included in the study. The best cut-off UAR concerned with renal survival was determined to be 9.94 with a specificity of 77.5% and a sensitivity of 61.5% (J, 0.390; AUC, 0.750). Then, the patients were divided into two groups labelled as low and high UAR ratios (≥ 9.94 and <9.94, respectively). More severe clinical manifestations and pathological lesions were observed in the high UAR group. Multivariate Cox regression analysis after adjusted for important clinicopathological parameters manifested that a high UAR was an independent prognostic biomarker for IgAN. (p = 0.036, HR =2.56, 95% CI: 1.07-6.16).
Conclusion: UAR might be a novel predictor for renal progression and contribute to targeted management.
Keywords: IgA nephropathy, IgAN, renal survival, uric acid to albumin ratio, UAR index

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact