ISSN: 1449-1907
Int J Med Sci 2023; 20(10):1316-1325. doi:10.7150/ijms.84899 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Clinical association and diagnostic significance of miRNA-29a and miRNA-147b in type 2 diabetes mellitus
1. Endocrine Hospital, Nghe An, Vietnam.
2. Department of Pathophysiology, Vietnam Military Medical University, Hanoi, Vietnam.
3. Centre for Genetics Counsulation and Cancer Screening, 108 Military Central Hospital, Hanoi, Vietnam.
4. Institute of Biomedicine and Pharmacy, Vietnam Military Medical University, Hanoi, Vietnam.
5. Internal Department, Vinh Medical University, Nghe An, Vietnam.
6. 103 Military Hospital, Vietnam Military Medical University, Hanoi, Vietnam.
Abstract
Background: Micro RNAs (miRs) expression is involved in the pathogenesis of type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM). This study investigates the expression levels of plasma miR-29a, miR-146a, and miR-147b and their correlations with clinical parameters in patients with T2DM.
Methods: 105 patients with T2DM who categorized either as newly diagnosed T2DM (n=52) or treated T2DM (n=53) and 93 healthy individuals were included in this study. The expression levels of miR-29a, miR-146a, and miR-147b were quantified by real-time PCR and analyzed for possible association with T2DM.
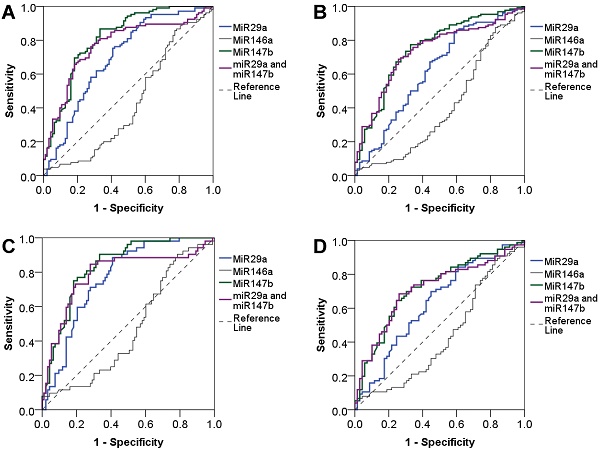
Results: The expressions of miR-29a and miR-147b were significantly increased in T2DM patients compared with healthy controls (P<0.0001). The expression levels of miR-29a in newly diagnosed T2DM patients were higher than that in the group of treated T2DM (P=0.002). The expression of studied miRs was correlated with several clinical parameters such as blood glucose levels, HbA1C, microalbuminuria, C-peptide, triglyceride levels as well as the HOMA-β index. The expression levels of miR-29a and miR-147b show a potential diagnostic performance to discriminate newly diagnostic T2DM (AUCs=0.77 and 0.84, respectively) and beta-cell dysfunction (AUCs= 0.62 and 0.75, respectively).
Conclusions: The plasma miR-29a and miR-147b expression levels in T2DM patients are significantly associated with T2DM while miR-146a shows poor evidence in relation to T2DM. miR-147b shows potential as a biomarker for the diagnosis of T2DM and pancreatic beta cell dysfunction.
Keywords: miR-29a, miR-146a, miR-147b, Type 2 diabetes mellitus, Beta-cell dysfunction

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact