ISSN: 1449-1907International Journal of Medical Sciences
Int J Med Sci 2023; 20(10):1300-1315. doi:10.7150/ijms.86990 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Comprehensive Analysis of Sideroflexin 4 in Hepatocellular Carcinoma by Bioinformatics and Experiments
1. Department of Gastroenterology, Institute of Liver and Gastrointestinal Diseases, Tongji Hospital, Tongji Medical College, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan, China.
2. Department of Geriatrics, Tongji Hospital, Tongji Medical College, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan, China.
†These authors contributed equally to this work.
Abstract
Background: Sideroflexins (SFXNs) are a family of highly conserved mitochondrial transporters which regulate iron homeostasis and mitochondrial respiratory chain. However, the roles and mechanisms of SFXNs in HCC remain unknown.
Methods: SFXNs expression and prognostic value in HCC was comprehensively analyzed. Proteins interacting with SFXN4 were analyzed in STRING database. The co-expression genes of SFXN4 were analyzed in cBioPortal database, and function of SFXN4 co-expression genes were annotated. The putative transcription factors and miRNA targeting SFXN4 were analyzed in NetworkAnalyst. The correlation between SFXN4 expression and immune infiltration was analyzed by ssGSEA. Cancer pathway activity and drug sensitivity related to SFXN4 were explored in GSCALite. The roles of SFXN4 in proliferation, migration and invasion of HCC were assessed in vitro and in vivo.
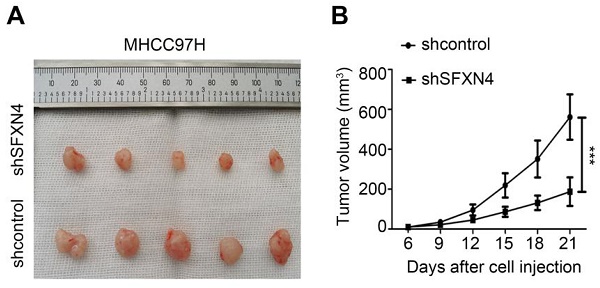
Results: SFXN4 was consistently elevated in HCC, positively correlated with clinicopathological characteristics and predicted poor outcome. Functional enrichment showed SFXN4 was mainly related to oxidative phosphorylation, reactive oxygen species and metabolic pathways. SFXN4 expression was regulated by multiple transcription factors and miRNAs, and SFXN4 expression in HCC was associated with several cancer pathways and drug sensitivity. SFXN4 expression correlated with immune infiltration in HCC. In vitro, knockdown of SFXN4 inhibited HCC proliferation, migration and invasion, and decreased the expression of cyclin D1 and MMP2. In vivo, knockdown of SFXN4 inhibited the growth of tumor xenografts in mice.
Conclusion: SFXN4 was upregulated in HCC, predicted poor prognosis, and may facilitate HCC development and progression via various mechanisms. For HCC, SFXN4 may provide both prognostic information and therapeutic potential.
Keywords: hepatocellular carcinoma, SFXN4, prognosis, proliferation, migration

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact