3.2
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1449-1907
Int J Med Sci 2023; 20(7):951-957. doi:10.7150/ijms.83993 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Utility of Serum Interleukine-6 Level in Empty Nose Syndrome
1. Department of Otolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery, Linkou Chang Gung Memorial Hospital, Taoyuan, Taiwan.
2. Graduate Institute of Clinical Medical Sciences, College of Medicine, Chang Gung University, Taoyuan, Taiwan.
Abstract
Objectives: Empty nose syndrome (ENS), a complication resulting from surgical procedures on turbinate tissue, is characterized by paradoxical nasal obstruction with wide nasal airways. Patients with ENS often also experience psychiatric symptoms, and psychiatric disorder detection remains dependent on subjective evaluation. Objective biomarkers for mental status assessment in patients with ENS are unestablished. This study aimed to evaluate the role of serum interleukin-6 (IL-6) levels in the mental status of patients with ENS.
Methods: Overall, 35 patients with ENS who underwent endonasal submucosal implantation surgery were prospectively included in the study. The Sino-Nasal Outcome Test-25 (SNOT-25), Empty Nose Syndrome 6-item Questionnaire (ENS6Q), Beck Anxiety Inventory (BAI), and Beck Depression Inventory-II (BDI-II) were used to assess the physical and psychiatric symptoms of these patients preoperatively, and 3, 6, and 12 months postoperatively. Serum IL-6 levels were analyzed 1 day before surgery.
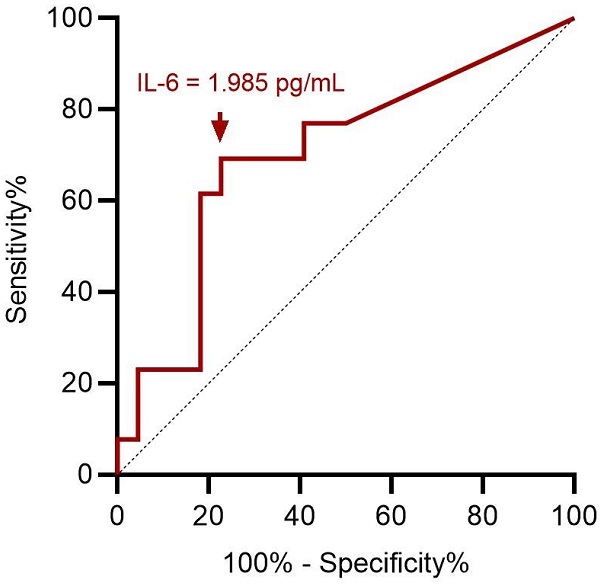
Results: All subjective assessments significantly improved 3 months after surgery and plateaued at 12 months. Patients with higher serum preoperative IL-6 levels tended to experience more severe depression. Regression analysis showed that a preoperative serum IL-6 level > 1.985 pg/mL was significantly correlated with severe depression status in patients with ENS (odds ratio = 9.76, p = 0.020).
Conclusions: ENS patients with higher preoperative serum IL-6 levels were more likely to have severe depressive burden. Since more suicidal thoughts or attempts were noted in these patients, timely treatment plan for patients with high levels of serum IL-6 is crucial and may consider psychotherapy after surgical treatment.
Keywords: interleukin-6 (IL-6), depression, Beck depression inventory-II (BDI-II), biomarker, empty nose syndrome

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact