ISSN: 1449-1907
Int J Med Sci 2023; 20(7):836-848. doi:10.7150/ijms.83009 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Identification of Three Cuproptosis-specific Expressed Genes as Diagnostic Biomarkers and Therapeutic Targets for Atherosclerosis
1. Department of Cardiology, the Eighth Affiliated Hospital of Sun Yat-sen University, Shenzhen, Guangdong 518033, China.
2. Department of Radiology, the Eighth Affiliated Hospital of Sun Yat-sen University, Shenzhen, Guangdong 518033, China.
3. Guangdong Innovative Engineering and Technology Research Center for Assisted Circulation, Shenzhen, Guangdong 518033, China.
4. NHC Key Laboratory of Assisted Circulation (Sun Yat-sen University), Guangzhou, Guangdong 510080, China.
# Contributed equally
Abstract
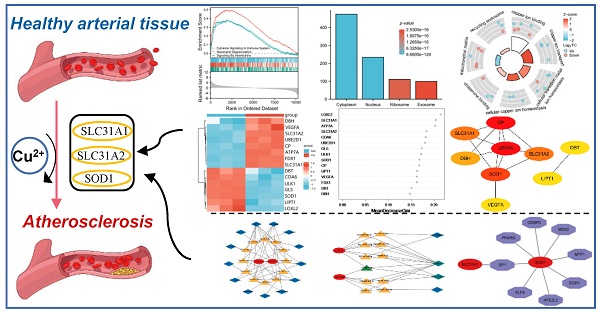
Atherosclerosis is a chronic, inflammatory disease characterized by a lipid-driven infiltration of inflammatory cells in large and medium arteries and is considered to be a major underlying cause of cardiovascular diseases. Cuproptosis, a novel form of cell death, is highly linked to mitochondrial metabolism and mediated by protein lipoylation. However, the clinical implication of cuproptosis-related genes (CRGs) in atherosclerosis remains unclear. In this study, genes collected from the GEO database intersected with CRGs were identified in atherosclerosis. GSEA, GO and KEGG pathway enrichment analyses were performed for functional annotation. Through the random forest algorithm and the construction of a protein-protein interaction (PPI) network, eight selected genes (LOXL2, SLC31A1, ATP7A, SLC31A2, COA6, UBE2D1, CP and SOD1) and a vital cuproptosis-related gene FDX1 were then further validated. Two independent datasets (GSE28829 (N = 29), GSE100927 (N = 104)) were collected to construct the signature of CRGs for validation in atherosclerosis. Consistently, the atherosclerosis plaques showed significantly higher expression of SLC31A1, SLC31A2 and lower expression of SOD1 than the normal intimae. The area under the curve (AUC) of SLC31A1, SLC31A2 and SOD1 performed well for the diagnostic validation in the two datasets. In conclusion, the cuproptosis-related gene signature could serve as a potential diagnostic biomarker for atherosclerosis and may offer novel insights into the treatment of cardiovascular diseases. Based on the hub genes, a competing endogenous RNA (ceRNA) network of lncRNA-miRNA-mRNA and a transcription factor regulation network were ultimately constructed to explore the possible regulatory mechanism in atherosclerosis.
Keywords: atherosclerosis, cuproptosis, cuproptosis-related gene (CRG), ceRNA network, bioinformatics analysis

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact