3.2
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1449-1907
Int J Med Sci 2023; 20(6):749-753. doi:10.7150/ijms.79539 This issue Cite
Short Research Communication
Molecular Autopsy in Asphyxia Deaths: Diagnostic Perspectives of miRNAs in the Evaluation of Hypoxia Response
1. Department of Medical Surgical Sciences and Translational Medicine, Sapienza University of Rome, Rome, Italy.
2. Department of Anatomical, Histological, Forensic and Orthopaedic Sciences, Sapienza University of Rome, Rome, Italy.
3. Department of Medicine, Surgery and Health, University of Trieste, Trieste, Italy.
Abstract
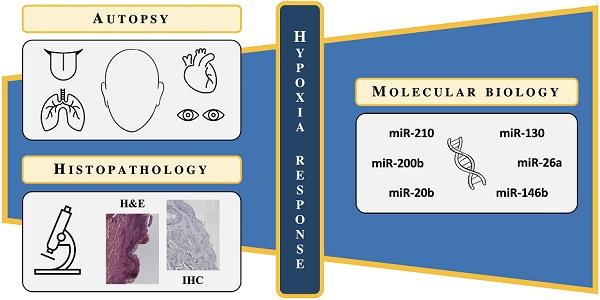
The forensic investigation of asphyxia deaths still poses a challenge due to the need to demonstrate vital exposure to hypoxic insult according to high levels of evidence. The pulmonary effects of hypoxia are complex and the understanding of the mechanisms underlying the acute pneumotoxicity induced by hypoxia is still incomplete. Redox imbalance has been suggested as the protagonist of the main acute changes in pulmonary function in the hypoxic context. The development of knowledge in biochemistry and molecular biology has allowed research in forensic pathology to identify some markers useful in immunohistochemical diagnostics of asphyxia deaths. Several studies have highlighted the diagnostic potential of markers belonging to the HIF-1α and NF-kB pathways. The central role of some highly specific microRNAs has recently been recognized in the complex molecular mechanisms involved in the hypoxia response; thus, several research activities are currently aimed at identifying miRNAs involved in the regulation of oxygen homeostasis (hypoxamiR). The aim of the manuscript is to identify, the miRNAs involved in the early stages of the cellular response to hypoxia, in order to characterize the possible implications in the forensic field of the determination of expression profiles. At present, more than 60 miRNAs involved in the hypoxia response with different expression profiles (upregulation and downregulation) have been identified. Despite the multiple and different effects on reprogramming following the hypoxic insult, the evaluation of the diagnostic implications of hypoxamiRs in the forensic field presupposes a specific treatment of the influences on HIF-1α regulation, cell cycle progression, DNA repair, and apoptosis.
Keywords: Asphyxia deaths, Hypoxia response, Forensic pathology, Molecular autopsy, HypoxamiRs

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact