3.2
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1449-1907
Int J Med Sci 2023; 20(4):468-481. doi:10.7150/ijms.78790 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Endothelial progenitor cell derived exosomes mediated miR-182-5p delivery accelerate diabetic wound healing via down-regulating PPARG
1. Stem Cell Research and Cellular Therapy Center, Affiliated Hospital of Guangdong Medical University, Zhanjiang 524001, China
2. Orthopedic Center, Affiliated Hospital of Guangdong Medical University, Zhanjiang, 524001, China
Abstract
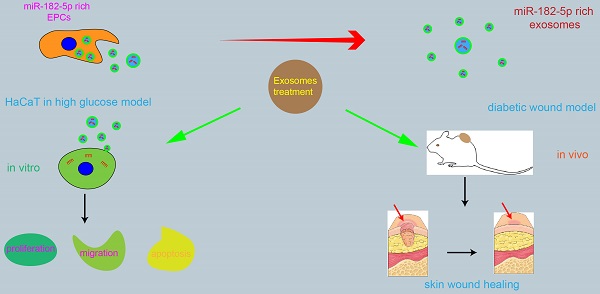
Diabetic wound is one of the most common and serious complications of diabetes, which is characterized by abnormal number and quality of wound repair related cells. Previous studies have shown that human endothelial progenitor cells derived exosomes (EPCs-EXO) can promote diabetic wound healing through modulating vascular endothelial cell function. The purpose of this study was to investigate the biological effects and molecular mechanisms of EPCs-EXO on diabetic wound healing. The regulation of EPCs-EXO on human immortalized epidermal cell line HaCaT in high glucose (HG) environment was evaluated. Our data showed that EPCs-EXO promoted the proliferation, migration, while inhibited apoptosis of HaCaTs challenged by HG via elevating miR-182-5p expression level in vitro. Skin wound healing was significantly enhanced by EPCs-EXO in diabetic mice. Moreover, bioinformatics analyses and luciferase reporter assay indicated that exosomal miR-182-5p was bound to PPARG 3' UTR sequence and inhibited the expression of PPARG. Collectively, our findings provided a new role of EPCs-EXO in the clinical treatment of diabetic skin wounds.
Diabetic wound is one of the most common and serious complications of diabetes, which is characterized by abnormal number and quality of wound repair related cells. Previous studies have shown that human endothelial progenitor cells derived exosomes (EPCs-EXO) can promote diabetic wound healing through modulating vascular endothelial cell function. The purpose of this study was to investigate the biological effects and molecular mechanisms of EPCs-EXO on diabetic wound healing. The regulation of EPCs-EXO on human immortalized epidermal cell line HaCaT in high glucose (HG) environment was evaluated. Our data showed that EPCs-EXO promoted the proliferation, migration, while inhibited apoptosis of HaCaTs challenged by HG via elevating miR-182-5p expression level in vitro. Skin wound healing was significantly enhanced by EPCs-EXO in diabetic mice. Moreover, bioinformatics analyses and luciferase reporter assay indicated that exosomal miR-182-5p was bound to PPARG 3' UTR sequence and inhibited the expression of PPARG. Collectively, our findings provided a new role of EPCs-EXO in the clinical treatment of diabetic skin wounds.
Keywords: Endothelial progenitor cell derived exosomes, diabetic wound healing, miR-182-5p, PPARG Endothelial progenitor cell derived exosomes, diabetic wound healing, miR-182-5p, PPARG

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact