ISSN: 1449-1907
Int J Med Sci 2023; 20(2):262-266. doi:10.7150/ijms.81381 This issue Cite
Review
Mechanism of CD38 via NAD+ in the Development of Non-alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease
1. Department of Cardiology, Beijing Hospital, National Center of Gerontology, Institute of Geriatric Medicine, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences, Beijing, China.
2. Department of Internal Medicine, The Affiliated Zhong Shan Hospital of Dalian University, Dalian, China.
3. Department of Cardiology, Central Hospital of Dalian University of Technology, Dalian, China.
4. Faculty of Medicine, Dalian University of Technology, Dalian, China.
Abstract
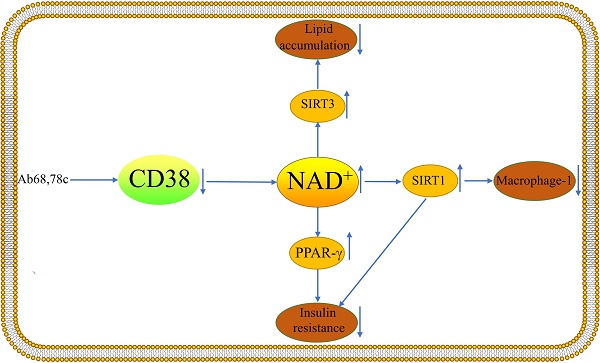
Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) is the most common chronic liver disease globally, and it can proceed to cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma, as well as cardiovascular disease, chronic renal disease, and other complications, resulting in a massive economic burden. At the moment, nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD+) is thought to be a possible treatment target for NAFLD, besides Cluster of differentiation 38(CD38) is the primary NAD+ degrading enzyme in mammals and may play a role in the pathophysiology of NAFLD. For example, CD38 regulates Sirtuin 1 activity and hence affects inflammatory responses. CD38 inhibitors enhance glucose intolerance and insulin resistance in mice and lipid accumulation in the liver is greatly decreased in CD38-deficient mice. This review describes the role of CD38 in the development of NAFLD in terms of Macrophage-1, insulin resistance, and abnormal lipid accumulation in order to offer recommendations for future NAFLD pharmacological trials.
Keywords: Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease, CD38, NAD+, Macrophage-1 Insulin resistance, Lipid accumulation.

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact