ISSN: 1449-1907
Int J Med Sci 2023; 20(2):247-253. doi:10.7150/ijms.79663 This issue Cite
Research Paper
A Nonlinear Relationship Between ALT Levels at Delivery and the Risk of Postpartum ALT Flares in Pregnant Women with Chronic Hepatitis B
1. Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Beijing Ditan Hospital, Capital Medical University, Beijing, 100015, China.
2. Hepatology clinic, Beijing Ditan Hospital, Capital Medical University, Beijing, 100015, China.
3. Department of General Medicine, Beijing Ditan Hospital, Capital Medical University, Beijing, 100015, China.
Abstract
Background: The aim of the present study was to investigate the association between alanine aminotransferase (ALT) levels at delivery and postpartum ALT flares among women with chronic hepatitis B (CHB).
Methods: Pregnant women with CHB from November 2008 to November 2017 were included in this retrospective study. Multivariable logistic regression analysis and a generalized additive model were performed to determine both linear and nonlinear relationships between ALT levels at delivery and postpartum ALT flares. Stratification analysis was performed to test for effect modifications in subgroups.
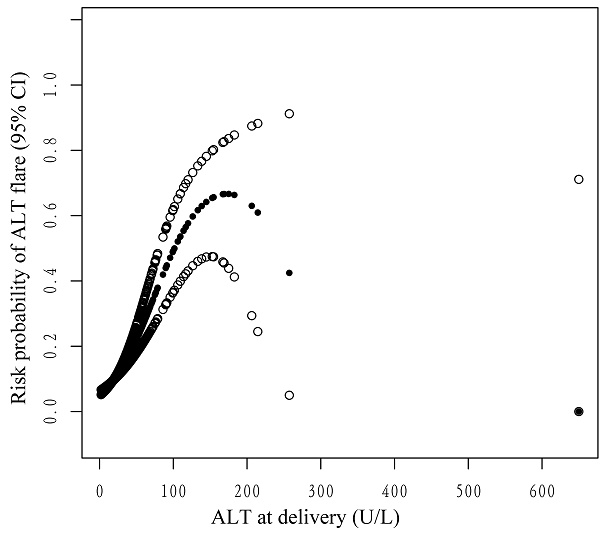
Results: A total of 2643 women were enrolled. Multivariable analysis indicated that ALT levels at delivery were positively associated with postpartum ALT flares (odds ratio (OR) 1.02, 95% confidence interval (CI) 1.01-1.02, P < 0.0001). When ALT levels were converted to a categorical variable, the ORs and 95% CIs in quartiles 3 and 4 versus quartile 1 were 2.26 (1.43-3.58) and 5.34 (3.48-8.22), respectively (P for trend < 0.001). When ALT levels were dichotomized into a categorical variable according to clinical cutoffs (40 U/L or 19 U/L), the ORs and 95% CIs were 3.06 (2.05-4.57) and 3.31 (2.53-4.35), respectively (P < 0.0001). The ALT level at delivery was also found to have a nonlinear relationship with postpartum ALT flares. The relationship followed an inverted U-shaped curve.
Conclusions: The ALT level at delivery was positively correlated with postpartum ALT flares in women with CHB when the ALT level was less than 182.8 U/L. The ALT cutoff (19 U/L) at delivery was more sensitive to predict the risk of ALT flares postpartum.
Keywords: Hepatitis B virus, Alanine Transaminase, Postpartum Period, Retrospective Studies, Pregnancy, Liver Function Tests

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact