3.2
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1449-1907
Int J Med Sci 2022; 19(14):2008-2021. doi:10.7150/ijms.78349 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Anticancer peptide Q7 suppresses the growth and migration of human endometrial cancer by inhibiting DHCR24 expression and modulating the AKT-mediated pathway
1. Department of Medical Research, Hsinchu MacKay Memorial Hospital, Hsinchu City 30071, Taiwan, ROC.
2. Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, MacKay Memorial Hospital, Taipei city 104, Taiwan, ROC.
3. Department of Medicine, MacKay Medical College, New Taipei City 25245, Taiwan, ROC.
4. Institute of Molecular Medicine and Bioengineering, National Yang Ming Chiao Tung University, Hsinchu City 30068, Taiwan, ROC.
5. Department of Biological Science and Technology, National Yang Ming Chiao Tung University, Hsinchu City 30068, Taiwan, ROC.
6. Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Hsinchu MacKay Memorial Hospital, Hsinchu City 30071, Taiwan, ROC.
7. Mackay Junior College of Medicine, Nursing and Management, Taipei City 11260, Taiwan, ROC.
Abstract
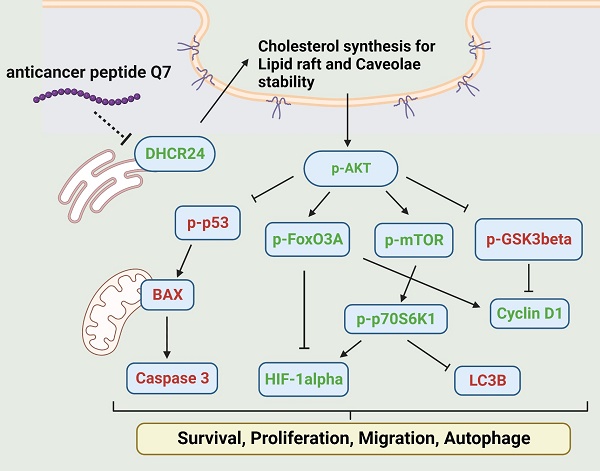
Endometrial cancer is one of the most common malignancy affecting women in developed countries. Resection uterus or lesion area is usually the first option for a simple and efficient therapy. Therefore, it is necessary to find a new therapeutic drug to reduce surgery areas to preserve fertility. Anticancer peptides (ACP) are bioactive amino acids with lower toxicity and higher specificity than chemical drugs. This study is to address an ACP, herein named Q7, which could downregulate 24-Dehydrocholesterol Reductase (DHCR24) to disrupt lipid rafts formation, and sequentially affect the AKT signal pathway of HEC-1-A cells to suppress their tumorigenicity such as proliferation and migration. Moreover, lipo-PEI-PEG-complex (LPPC) was used to enhance Q7 anticancer activity in vitro and efficiently show its effects on HEC-1-A cells. Furthermore, LPPC-Q7 exhibited a synergistic effect in combination with doxorubicin or paclitaxel. To summarize, Q7 was firstly proved to exhibit an anticancer effect on endometrial cancer cells and combined with LPPC efficiently improved the cytotoxicity of Q7.
Keywords: endometrial cancer, ACP, anticancer peptides, DHCR24, 24-Dehydrocholesterol Reductase, lipid rafts, AKT pathway, LPPC, lipo-PEI-PEG-complex

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact