3.2
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1449-1907
Int J Med Sci 2022; 19(13):1920-1928. doi:10.7150/ijms.63973 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Identification of Novel Phenotypes Correlated with CKD: A Phenotype-Wide Association Study
1. Cardiology department, First affiliated hospital of Sun Yat-Sen University.
2. NHC Key Laboratory of Assisted Circulation (Sun Yat-Sen University).
3. Department of Urology, Sun Yat-Sen Memorial Hospital, Sun Yat-Sen University.
4. Guangdong Provincial Key Laboratory of Malignant Tumor Epigenetics and Gene Regulation, Sun Yat-Sen Memorial Hospital.
5. Department of Statistical Science, School of Mathematics, Southern China Center for Statistical Science, Sun Yat-Sen University.
6. Department of Urology, the Third Affiliated Hospital of Sun Yat-Sen University.
*Yifen Lin and Jianqiu Kong contributed equally to the study.
Abstract
Background: A comprehensive understanding of phenotypes related to CKD will facilitate the identification and management of CKD. We aimed to panoramically test and validate associations between multiple phenotypes and CKD using a phenotype-wide association study (PheWAS).
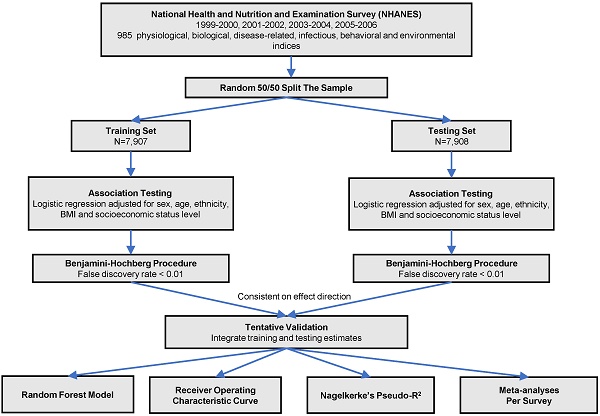
Methods: 15,815 subjects from cross-sectional cohorts of the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (1999-2006) were randomly 50:50 split into training and testing sets. CKD was defined as eGFR < 60 mL/min/1.73m2. We performed logistic regression analyses between each of 985 phenotypes with CKD in the training set (false discovery rate < 1%) and validated in the testing set (false discovery rate < 1% ). Random forest (RF) model, Nagelkerke's Pseudo-R2, and the area under the receiver operating characteristic (AUROC) were used to validate the identified phenotypes.
Results: We identified 18 phenotypes significantly related to CKD, among which retinol, red cell distribution width (RDW), and C-peptide were less researched. The top 5 identified phenotypes were blood urea nitrogen (BUN), homocysteine (HCY), retinol, parathyroid hormone (PTH), and osmolality in RF importance ranking. Besides, BUN, HCY, PTH, retinol, and uric acid were the most important phenotypes based on Pseudo-R2. AUROC of the RF model was 0.951 (full model) and 0.914 (top 5 phenotypes).
Conclusion: Our study demonstrated associations between multiple phenotypes with CKD from a holistic view, including 3 novel phenotypes: retinol, RDW, and C-peptide. Our findings provided valid evidence for the identification of novel biomarkers for CKD.
Keywords: chronic kidney disease, phenotype-wide association study, retinol, red cell distribution width, C-peptide.

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact