ISSN: 1449-1907
Int J Med Sci 2022; 19(12):1796-1805. doi:10.7150/ijms.68646 This issue Cite
Research Paper
The Inhibition of Adipose-Derived Stem Cells on the Invasion of Keloid Fibroblasts
1. Department of Dermatology, 2nd Affiliated Hospital, School of Medicine, Zhejiang University, Hangzhou, Zhejiang, China.
2. Department of Dermatology, Ningbo Medical Center Lihuili Hospital, Ningbo, Zhejiang, China.
3. Department of Dermatology, The Central Hospital of Lishui City, Lishui, Zhejiang, China.
Abstract
Background: Keloids represent the dysregulation of cutaneous wound healing caused by aberrant fibroblast activities. Adipose-derived stem cells have been recognized as a promising treatment for keloids. However, the molecular mechanisms have not been fully elucidated.
Objectives: to explicitly demonstrate the relationship between adipose-derived stem cells alleviating keloids and alterations of Col-1, Col-3, CTGF, and P-4-HB.
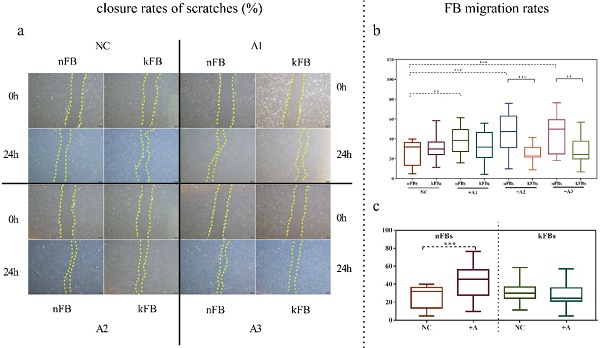
Methods: Skin biopsies were obtained from 10 keloid patients and 9 healthy volunteers. Fibroblasts isolated from all samples were divided into two groups, one co-cultured with adipose-derived stem cells and the other grown independently. We compared the wound-healing rates, fibroblast survival rates, apoptosis rates, mRNA expressions, and protein levels of Col-1, Col-3, CTGF, and P-4-HB between separated groups.
Results: We found no significant differences between normal fibroblasts and keloid fibroblasts in terms of wound-healing rate, survival rate, or apoptosis rate at the baseline. With adipose-derived stem cells, wound-healing rate and survival rate of normal fibroblasts were promoted, whereas in keloid fibroblasts, they were reduced. The apoptosis rate of normal fibroblasts and keloid fibroblasts were restrained, with the restraint in keloid fibroblasts being more evident. The protein levels of Col-3, CTGF, and P-4-HB were lower in keloid fibroblasts co-cultured with adipose-derived stem cells than in normal fibroblasts under similar conditions.
Conclusions: Adipose-derived stem cells strongly suppressed keloid fibroblasts' proliferative and invasive behavior. However, adipose-derived stem cells negatively regulated keloid fibroblast apoptosis. Adipose-derived stem cells can be a potential keloid therapy worth further investigation.
Keywords: keloids, adipose-derived stem cells, fibroblasts, collagen, wound healing

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact