ISSN: 1449-1907
Int J Med Sci 2022; 19(12):1724-1731. doi:10.7150/ijms.77017 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Multiple proliferation signaling pathways are modulated by octacalcium phosphate in osteoblasts
1. Department of Physiology, Konkuk University School of Medicine, Chungju, Republic of Korea.
2. Dental biomaterials science, School of dentistry and dental research institute, Seoul National University, 101 Daehak-ro, Jongno-gu, Seoul, Republic of Korea.
3. HudensBio Co., Ltd, 318 Cheomdanyeonsin-ro, Buk-gu, Gwangju 61088, Republic of Korea.
4. Department of Biomedical Engineering, Yeungnam University, Daegu 42415, Republic of Korea.
Abstract
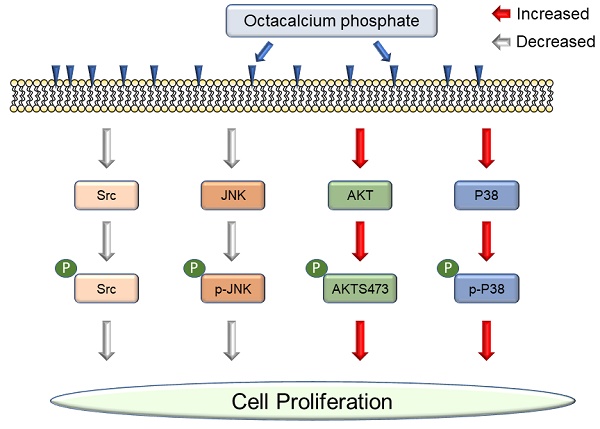
Octacalcium phosphate (OCP), a type of bioactive ceramics, may be associated with dentine, tooth apatite, and especially bone generation, and promotes wound healing after fracture. Recently, commercial bone grafting products containing a large amount of OCP material have been released because OCP can be synthesized in large quantities. It is reported to increase cell proliferation, but the interaction between OCP and cell signaling pathways is still unclear. In this study, first, we demonstrated OCP mediated cell signaling pathways with only purified OCP materials. OCP regulated P38, JNK (c-Jun N-terminal kinase), Src, and AKT (protein kinase B) signaling pathways. OCP crystals appeared in the characteristic ribbon shape but varied by several tens of micrometers in size. The X-ray diffraction pattern was the same as previously reported. We studied two concentrations of OCP (10 mg/ml and 20 mg/ml) to understand whether the effect of OCP on cell signaling pathways is dose dependent. We confirmed that OCP treatment affected cell proliferation and alkaline phosphatase and disrupted Src phosphorylation but did not change the total protein level. P38 phosphorylation was activated with OCP treatment and inhibited by SB203580, but P38 total protein level did not change. OCP inhibited JNK phosphorylation signaling, whereas PD98509 inhibited JNK phosphorylation with or without OCP. Interestingly, the AKT total level decreased after OCP treatment, but AKT phosphorylation increased considerably. Our results demonstrate that OCP materials modulate cell signaling pathways and increase cell proliferation.
Keywords: Octacalcium phosphate, Cell signaling pathway, Cell proliferation, ALP activity

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact