ISSN: 1449-1907
Int J Med Sci 2022; 19(11):1628-1630. doi:10.7150/ijms.76615 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Superficial Venous-Associated Inflammation from Direct IV Administration of RRx-001 in Rats
1. EpicentRx Inc., 11099 North Torrey Pines Road Suite 160, La Jolla, CA 92037, USA.
2. Sinclair Research, 562 State Road DD, Auxvasse, MO 65231, USA.
Abstract
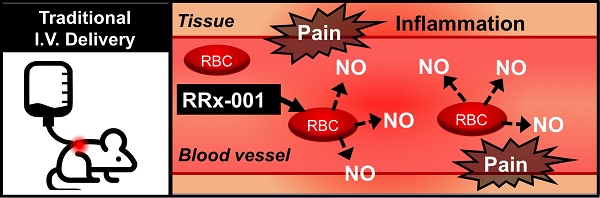
RRx-001 is a small molecule NLRP3 inflammasome inhibitor with anti-CD47 and antiangiogenic/vascular normalization properties in a Phase 3 clinical trial that has been designated as a drug-device combination by the FDA. In the Phase 1 first-in-man dose escalation clinical trial, where RRx-001 was given by direct intravenous (IV) infusion, the main adverse event was a sterile painful infusion phlebitis (IP). Less pain was experienced when RRx-001 was infused at a slower rate over multiple hours which was impractical on an outpatient basis. In Phase 2, for reasons of convenience and safety, RRx-001 was co-administered with an aliquot of autologous blood from an ex-vivo device called the eLOOP on the premise that RRx-001 binds to hemoglobin on red blood cells (RBCs), making it unavailable to directly interact with venous nociceptors. Phlebitis has the potential to progress to deep venous thrombosis or septic thrombophlebitis or post-thrombotic syndrome in hypercoagulable and immunosuppressed cancer patients. In this 13-week toxicology study of once weekly IV RRx-001 administration to Wistar Han rats followed by a recovery period of 28 days. The main observed toxicity was a significant inflammatory response in the vein wall, consistent with superficial venous thrombosis observed in man. Due to this development, direct IV infusion of RRx-001 is relatively contraindicated in favor of co-administration with autologous blood.
Keywords: Intravenous infusion, phlebitis, small molecule, RRx-001, drug-device combination

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact