3.2
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1449-1907
Int J Med Sci 2022; 19(7):1184-1197. doi:10.7150/ijms.74569 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Rotenone, an environmental toxin, causes abnormal methylation of the mouse brain organoid's genome and ferroptosis
1. School of Environmental and Chemical Engineering, Shanghai University, Shanghai 200444, China.
2. Department of Dermatology, Yueyang Hospital of Integrated Traditional Chinese and Western Medicine, Shanghai University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Shanghai 200437, China.
3. Department of Neurology, Shanghai General Hospital, Shanghai Jiao Tong University School of Medicine, Shanghai 200080, China.
4. Shanghai Geriatric Institute of Chinese Medicine, Shanghai University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Shanghai 200031, China.
5. School of Life Science and Technology, Tongji University, Shanghai 200092, China.
*These authors contributed equally to this work and shared the first authorship.
Abstract
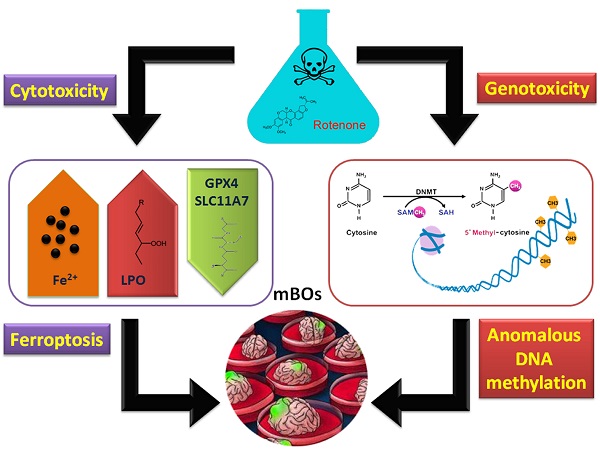
More and more reports have pointed out that rotenone, as an insecticide, has high neurotoxicity and reproductive toxicity to livestock and mammals. As a highly physiological correlation system of internal organs, quasi-organs have great potential in the fields of drug toxicity and efficacy test, toxicology research, developmental biology and so on. In this study, brain organs (mBOs) derived from mouse neural stem cells were used to investigate the effects of rotenone on the physiological activity and epigenetic modification of mBOs. At the same time, Rotenone could significantly stimulate the increase of the concentration of LPO, lactic acid and hydroxyl radical in mBOs, and inhibit the expression of neuronal marker Tuj1, CHAT, PAX6 and so on. Further analysis showed that Rotenonem could induce mitochondrial damage in mBOs. The results of qPCR and Western blot showed that Rotenone could up-regulate the expressions of ferroptosis promoting protein p53, Cox2 and so on, while inhibit the expressions of negative regulatory protein of ferroptosis GPX4, FTH1, SLC7A11. In addition, the results of RRBS-Seq sequencing showed that the methylation modification at DMR level in Rotenone-treated mBOs group was significantly higher than that in Ctrl group. The results of KEGG analysis showed that compared with Ctrl, the genes with hypermethylation of promoter and Genebody in Rotenone-treated mBOs were mainly located in the Neuro active ligand-receptor interaction signal transduction pathway. In summary, rotenone can significantly lead to abnormal methylation of mouse brain organs, and lead to the loss of normal physiological function of neurons by inducing ferroptosis.
Keywords: Rotenone, brain organoid, genome methylation modification, ferroptosis, environmental pollution and ecotoxicity

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact