3.2
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1449-1907
Int J Med Sci 2022; 19(5):878-892. doi:10.7150/ijms.71780 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Nephronectin promotes cardiac repair post myocardial infarction via activating EGFR/JAK2/STAT3 pathway
1. Department of Cardiology, Shanghai Jiao Tong University Affiliated Sixth People's Hospital, Shanghai 200233, China
2. Department of Geriatrics, Shanghai Jiao Tong University Affiliated Sixth People's Hospital, Shanghai 200233, China
* These authors contributed equally to this work.
Abstract
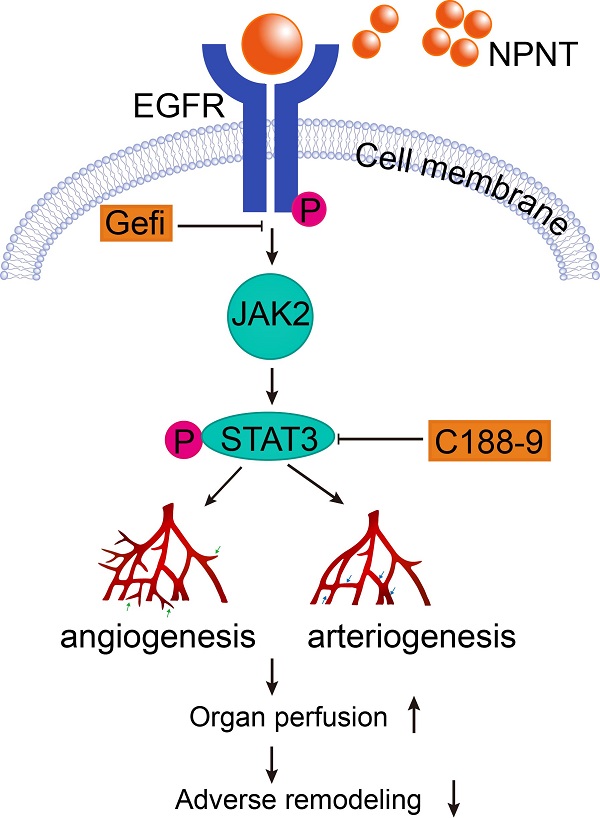
Background: ECM proteins are instrumental for angiogenesis, which plays momentous roles during development and repair in various organs, including post cardiac insult. After a screening based on an open access RNA-seq database, we identified Nephronectin (NPNT), an extracellular protein, might be involved in cardiac repair post myocardial infarction (MI). However, the specific impact of nephronectin during cardiac repair in MI remains elusive.
Methods and Results: In the present study, we established a system overexpressing NPNT locally in mouse heart by utilizing a recombinant adeno-associated virus. One-to-four weeks post MI induction, we observed improved cardiac function, limited infarct size, alleviated cardiac fibrosis, with promoted angiogenesis in infarct border zone in NPNT overexpressed mice. And NPNT treatment enhanced human umbilical vascular endothelial cell (HUVEC) migration and tube formation, putatively through advocating phosphorylation of EGFR/JAK2/STAT3. The migration and capillary-like tube formation events could be readily revoked by EGFR or STAT3 inhibition. Notably, phosphorylation of EGFR, JAK2 and STAT3 were markedly upregulated in AAV2/9-cTnT-NPNT-treated mice with MI.
Conclusions: Our study thus identifies the beneficial effects of NPNT on angiogenesis and cardiac repair post MI by enhancing the EGFR/JAK2/STAT3 signaling pathway, implying the potential therapeutic application of NPNT on myocardial dysfunction post MI.
Keywords: Nephronectin, myocardial infarction, epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR), angiogenesis, cardiac repair

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact