3.2
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1449-1907
Int J Med Sci 2021; 18(16):3821-3830. doi:10.7150/ijms.65976 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy Attenuates Burn-Induced Denervated Muscle Atrophy
1. Department of Anesthesiology, Kaohsiung Municipal Ta-Tung Hospital, Kaohsiung, Taiwan.
2. Department of Anesthesiology, Kaohsiung Medical University Hospital, Kaohsiung, Kaohsiung Medical University, Taiwan.
3. School of Medicine, College of Medicine, Kaohsiung Medical University, Kaohsiung, Taiwan.
4. Department of General Medicine, Kaohsiung Medical University Hospital, Kaohsiung Medical University, Kaohsiung, Taiwan.
5. Division of Plastic Surgery, Department of Surgery, Kaohsiung Medical University Hospital, Kaohsiung Medical University, Kaohsiung, Taiwan.
6. Department of Surgery, School of Medicine, College of Medicine, Kaohsiung Medical University, Kaohsiung, Taiwan.
7. Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy Center, Kaohsiung Medical University Hospital, Kaohsiung Medical University, Kaohsiung, Taiwan.
8. Department of Anesthesiology, School of Medicine, College of Medicine, Kaohsiung Medical University, Kaohsiung, Taiwan.
#The first authors contributed equally to this work.
Abstract
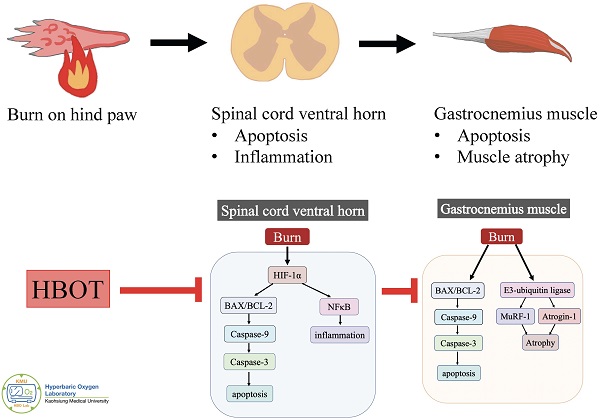
Background: Neuronal apoptosis and inflammation in the ventral horn of the spinal cord contribute to denervated muscle atrophy post-burn. Hyperbaric oxygen therapy (HBOT) exerts anti-inflammation and neuroprotection. Furthermore, hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF)-1α has been reported to promote inflammation and apoptosis. We investigated the therapeutic potential of HBOT and the role of HIF-1α post-burn.
Methods: Sprague-Dawley rats were divided into three groups: a control group, an untreated burn group receiving burn and sham treatment, and a HBOT group receiving burn injury and HBOT. The burn injury was induced with 75ºC ± 5ºC at the right hindpaw. HBOT (100% oxygen at 2.5 atmosphere, 90 min/day) and sham HBOT (21% oxygen at 1 atmosphere, 90 min/day) was started on day 28 after burn injury and continued for 14 treatments (days 28-41). Incapacitance (hind limb weight bearing) testing was conducted before burn and weekly after burn. At day 42 post-burn, the gastrocnemius muscle and the spinal cord ventral horn were analyzed.
Results: HBOT improved burn-induced weight bearing imbalance. At day 42 post-burn, less gastrocnemius muscle atrophy and fibrosis were noted in the HBOT group than in the untreated burn group. In the ventral horn, HBOT attenuated the neuronal apoptosis and glial activation post-burn. The increases in phosphorylated AKT/mTOR post-burn were reduced after HBOT. HBOT also inhibited HIF-1α signaling, as determined by immunofluorescence and western blot.
Conclusions: HBOT reduces burn-induced neuronal apoptosis in the ventral horn, possibly through HIF-1α signaling.
Keywords: Burn injury, Hyperbaric oxygen therapy, Neuronal apoptosis, Denervated muscle atrophy, Hypoxia-inducible factor-1α

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact