3.2
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1449-1907
Int J Med Sci 2021; 18(16):3738-3743. doi:10.7150/ijms.62871 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Fat-to-muscle Ratio: A New Indicator for Coronary Artery Disease in Healthy Adults
1. Department of Family Medicine, Yeouido St. Mary's Hospital, College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Seoul, Republic of Korea.
2. Division of Cardiology, Department of Internal Medicine, St. Vincent's Hospital, College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Suwon-si, Republic of Korea.
3. Department of Family Medicine, St. Vincent's Hospital, College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Suwon-si, Republic of Korea.
Abstract
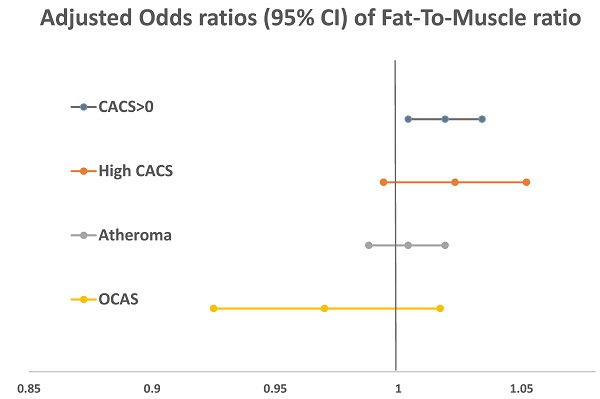
Background: Coronary artery disease (CAD) is an important issue in public health. Previous studies have shown that the ratio of fat to muscle mass is a significant predictor of metabolic disease, and it is known to be associated with atherosclerosis. In this study, we evaluated the association between the fat-to-muscle ratio (FMR) and CAD in healthy adults.
Methods: A total of 617 participants without diabetes mellitus, hypertension, known CAD, or stroke who visited the Health Promotion Center from 2009 to 2018 were included in this study. Computed tomography imaging and bioelectrical impedance analysis were used to ascertain the coronary artery calcium (CAC) score, degree of CAD, and FMR.
Results: Univariate logistic regression analysis showed that old age, male sex, smoking history, creatinine, aspartate aminotransferase, gamma-glutamyl transferase, uric acid, total cholesterol, and low-density lipoprotein cholesterol were significantly associated with CAC. After adjusting for potential confounding covariates, the presence of CAC was independently associated with FMR (OR, 1.014; 95% CI, 1.002-1.026; p = 0.019. The association was maintained even after adjusting for body mass index and waist circumference (odds ratio, 1.019; 95% confidence interval, 1.004 -1.034; P = 0.012).
Conclusion: In this study, a high FMR was significantly associated with CAC. A large-scale prospective study on the association with FMR and cardiovascular diseases is necessary to confirm this relationship.
Keywords: Skeletal muscle, body fat, coronary artery disease

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact