3.2
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1449-1907
Int J Med Sci 2021; 18(15):3599-3608. doi:10.7150/ijms.62386 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Predictive performance of eLIFT for liver inflammation and fibrosis in chronic liver diseases
1. Department of Hepatobiliary Medicine, Shanghai Public Health Clinical Center, Fudan University, Shanghai 201508, China.
2. Department of Integrative Medicine, Shanghai Public Health Clinical Center, Fudan University, Shanghai 201508, China.
3. Department of Ultrasound, Shanghai Public Health Clinical Center, Fudan University, Shanghai 201508, China.
#These authors have contributed equally to this work.
Abstract
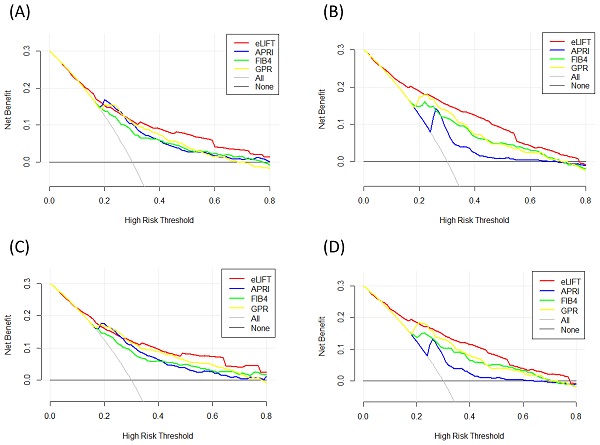
Objective: The easy liver fibrosis test (eLIFT) is a novel predictor of liver fibrosis in chronic liver disease (CLD). This study aimed to evaluate the predictive value of the eLIFT for liver inflammation and fibrosis in CLD patients.
Methods: We enrolled 1125 patients with CLD who underwent liver biopsy. The predictive accuracy for liver inflammation and fibrosis of the eLIFT was assessed and compared to that of the aspartate aminotransferase-to-platelet ratio index (APRI), fibrosis-4 score (FIB-4), and gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase-to-platelet ratio (GPR) by ROC (Receiver Operating Characteristic) analysis and decision curve analysis (DCA).
Results: The areas under the ROC curves (AUROCs) of the eLIFT for assessing liver inflammation G ≥ 2 and G ≥ 3 were 0.77 (0.75-0.80) and 0.81 (0.79-0.84), with cut-offs of 8.0 and 11.0, respectively. The AUROCs of the eLIFT for predicting fibrosis stages S ≥ 2 and S4 were 0.72 (0.70-0.76) and 0.76 (0.72-0.80), with cut-offs of 9.0 and 10.0, respectively. In discriminating G≥2 inflammation, the AUROC of the eLIFT was better than that of the FIB-4, with no difference compared with the GPR, but lower than that of the APRI. When discriminating G≥3 inflammation, the AUROC of the eLIFT was comparable to that of the APRI and GPR but superior to that of the FIB-4. There were no significant differences between the four indexes for predicting S≥2 and S4.
Conclusion: The eLIFT is a potentially useful noninvasive predictor of liver inflammation and fibrosis in patients with CLD.
Keywords: eLIFT, GPR, liver fibrosis, chronic liver disease

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact