3.2
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1449-1907
Int J Med Sci 2021; 18(15):3533-3543. doi:10.7150/ijms.62021 This issue Cite
Review
Possible mechanisms of cholesterol elevation aggravating COVID-19
1. Department of Cardiology, Heart Center, Zhujiang Hospital, Southern Medical University, 235 Industrial Avenue, Guangzhou, 510282, Guangdong, People's Republic of China.
2. Department of Cardiology, Raoping County People's Hospital, 161 Caichang Street, Huanggang Town, Chaozhou, 515700, Guangdong, People's Republic of China.
3. Department of Cardiology, Affiliated Boai Hospital of Zhongshan, Southern Medical University, No. 6, Chenggui Road, East District, Zhongshan, 528403, Guangdong, People's Republic of China.
4. School of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Southern Medical University, No. 6, Chenggui Road, East District, Zhongshan, 528403, Guangdong, People's Republic of China.
5. Zhujiang Hospital, Southern Medical University/The Second School of Clinical Medicine, Southern Medical University, No. 6, Chenggui Road, East District, Zhongshan, 528403, Guangdong, People's Republic of China.
UGS: undergraduate students; MD: medical doctor.
#These authors contributed equally to this work.
Abstract
Importance: Despite the availability of a vaccine against the severe acute respiratory syndrome-coronavirus-2 (SARS-CoV-2), humans will have to live with this virus and the after-effects of the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) infection for a long time. Cholesterol plays an important role in the infection and prognosis of SARS-CoV-2, and the study of its mechanism is of great significance not only for the treatment of COVID-19 but also for research on generic antiviral drugs.
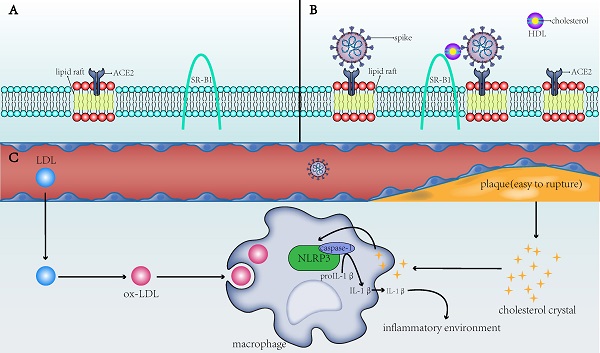
Observations: Cholesterol promotes the development of atherosclerosis by activating NLR family pyrin domain containing 3 (NLRP3), and the resulting inflammatory environment indirectly contributes to COVID-19 infection and subsequent deterioration. In in vitro studies, membrane cholesterol increased the number of viral entry sites on the host cell membrane and the number of angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) receptors in the membrane fusion site. Previous studies have shown that the fusion protein of the virus interacts with cholesterol, and the spike protein of SARS-CoV-2 also requires cholesterol to enter the host cells. Cholesterol in blood interacts with the spike protein to promote the entry of spike cells, wherein the scavenger receptor class B type 1 (SR-B1) plays an important role. Because of the cardiovascular protective effects of lipid-lowering therapy and the additional anti-inflammatory effects of lipid-lowering drugs, it is currently recommended to continue lipid-lowering therapy for patients with COVID-19, but the safety of extremely low LDL-C is questionable.
Conclusions and Relevance: Cholesterol can indirectly increase the susceptibility of patients to SARS-CoV-2 and increase the risk of death from COVID-19, which are mediated by NLRP3 and atherosclerotic plaques, respectively. Cholesterol present in the host cell membrane, virus, and blood may also directly participate in the virus cell entry process, but the specific mechanism still needs further study. Patients with COVID-19 are recommended to continue lipid-lowering therapy.
Keywords: cholesterol, LDL-C, COVID-19, membrane fusion, lipid-lowering drugs

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact