3.2
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1449-1907
Int J Med Sci 2021; 18(15):3516-3525. doi:10.7150/ijms.60135 This issue Cite
Research Paper
PLK1 Inhibition Induces Immunogenic Cell Death and Enhances Immunity against NSCLC
1. Cancer Center, Union Hospital, Tongji Medical College, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan 430022, P. R. China.
2. Department of Integrated Traditional Chinese and Western Medicine, Union Hospital, Tongji Medical College, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan 430022, P. R. China.
*Authors contributed equally to this work.
Abstract
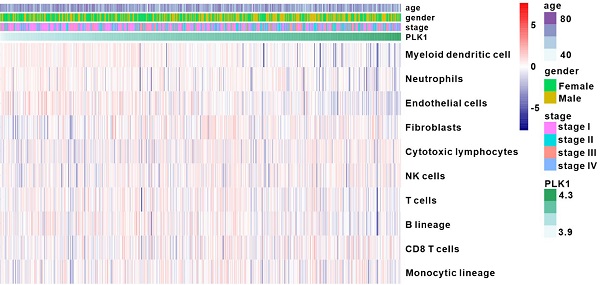
PLK1 inhibitors were shown, in vitro and in vivo, to possess inhibitory activities against non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC), and such inhibition has been proven by clinical trials. However, it remains unclear whether and how the immune microenvironment is associated with the action. In this study, we found that inhibiting PLK1 could alter the tumor immune microenvironment by increasing DC maturation, and enriching T cells infiltration. PLK1 inhibitors, serving as immunogenic cell death (ICD) inducers, indirectly activated DCs, instead of directly acting on DC cells, through the surface expression of costimulatory molecules on and enhanced phagocytosis by DCs. Furthermore, upon targeting PLK1, tumor cells that had undergone ICD were converted into an endogenous vaccine, which triggered the immune memory responses and protected the mice from tumor challenge. Collectively, these results suggested that the PLK1 inhibitor might function as an immune modulator in antitumor treatment.
Keywords: PLK1, ICD, immune infiltrates, NSCLC

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact