ISSN: 1449-1907
Int J Med Sci 2021; 18(15):3470-3477. doi:10.7150/ijms.63180 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Sex Difference in the Associations among Obesity-Related Indices with Metabolic Syndrome in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
1. Department of Laboratory Medicine, Kaohsiung Medical University Hospital, Kaohsiung Medical University, Kaohsiung, Taiwan.
2. Department of post baccalaureate medicine, Kaohsiung Medical University, Kaohsiung, Taiwan.
3. Department of Medical Imaging, Kaohsiung Medical University Hospital, Kaohsiung Medical University, Kaohsiung, Taiwan.
4. Division of Endocrinology and Metabolism, Department of Internal Medicine, Kaohsiung Medical University Hospital, Kaohsiung Medical University, Kaohsiung, Taiwan.
5. Department of Medical Laboratory Science and Biotechnology, College of Health Sciences, Kaohsiung Medical University, Kaohsiung, Taiwan.
6. Department of Internal Medicine, Kaohsiung Municipal Siaogang Hospital, Kaohsiung Medical University, Kaohsiung, Taiwan.
7. Division of Nephrology, Department of Internal Medicine, Kaohsiung Medical University Hospital, Kaohsiung Medical University, Kaohsiung, Taiwan.
8. Faculty of Medicine, College of Medicine, Kaohsiung Medical University, Kaohsiung, Taiwan.
Abstract
Background: The aim of this study was to investigate the associations among obesity-related indices and MetS in diabetic patients, and explore sex differences in these associations.
Methods: Patients with type 2 DM were included from two hospitals in southern Taiwan. The Adult Treatment Panel III criteria for an Asian population were used to define MetS. In addition, the following obesity-related indices were evaluated: waist-to-height ratio, waist-hip ratio (WHR), conicity index (CI), body mass index (BMI), body roundness index, body adiposity index, lipid accumulation product (LAP), abdominal volume index, visceral adiposity index (VAI), abdominal volume index and triglyceride-glucose index.
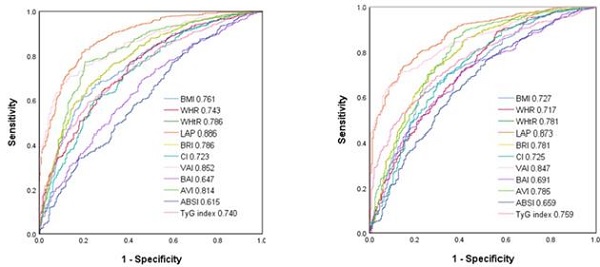
Results: A total of 1,872 patients with type 2 DM (mean age 64.0 ± 11.3 years, 808 males and 1,064 females) were enrolled. The prevalence rates of MetS were 59.8% and 76.4% in the males and female (p < 0.001), respectively. All of the obesity-related indices were associated with MetS in both sex (all p < 0.001). LAP and BMI had the greatest areas under the receiver operating characteristic curves in both sex. In addition, the interactions between BMI and sex (p = 0.036), WHR and sex (p = 0.016), and CI and sex (p = 0.026) on MetS were statistically significant.
Conclusions: In conclusion, this study demonstrated significant relationships between obesity-related indices and MetS among patients with type 2 DM. LAP and VAI were powerful predictors in both sex. The associations of BMI, WHR and CI on MetS were more significant in the men than in the women.
Keywords: sex difference, obesity-related indices, metabolic syndrome, diabetes mellitus

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact