3.2
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1449-1907
Int J Med Sci 2021; 18(13):2930-2942. doi:10.7150/ijms.51439 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Enhancement of cytotoxicity and induction of apoptosis by cationic nano-liposome formulation of n-butylidenephthalide in breast cancer cells
1. Institute of Medicine, Chung Shan Medical University, Taichung, 40201, Taiwan, ROC.
2. Department of Medical Laboratory and Biotechnology, Chung Shan Medical University, Taichung, 40201, Taiwan, ROC.
3. Agricultural Biotechnology Research Center, Academia Sinica, Taipei, 11529, Taiwan, ROC.
4. Department of Biological Science and Technology, National Chiao Tung University, Hsinchu, 30010, Taiwan, ROC.
5. Institute of Molecular Medicine and Bioengineering, National Chiao Tung University, Hsinchu, 30010, Taiwan, ROC.
6. Division of Nephrology, Department of Internal Medicine, Ditmanson Medical Foundation Chia-Yi Christian Hospital, Chia-Yi, 60002, Taiwan, ROC.
7. Department of Hospital and Health Care Administration, Chia Nan University of Pharmacy and Science, Tainan, 71710, Taiwan, ROC.
8. Clinical Laboratory, Chung Shan Medical University Hospital, Taichung, 40201, Taiwan, ROC.
Abstract
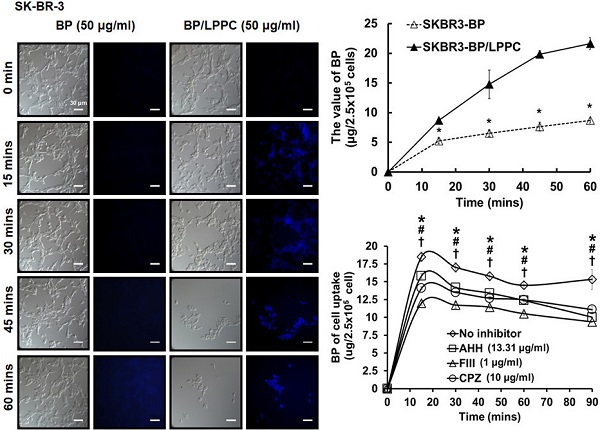
Breast cancer is the second most common malignancy in women. Current clinical therapy for breast cancer has many disadvantages, including metastasis, recurrence, and poor quality of life. Furthermore, it is necessary to find a new therapeutic drug for breast cancer patients to meet clinical demand. n-Butylidenephthalide (BP) is a natural and hydrophobic compound that can inhibit several tumors. However, BP is unstable in aqueous or protein-rich environments, which reduces the activity of BP. Therefore, we used an LPPC (Lipo-PEG-PEI complex) that can encapsulate both hydrophobic and hydrophilic compounds to improve the limitation of BP. The purpose of this study is to investigate the anti-tumor mechanisms of BP and BP/LPPC and further test the efficacy of BP encapsulated by LPPC on SK-BR-3 cells. BP inhibited breast cancer cell growth, and LPPC encapsulation (BP/LPPC complex) enhanced the cytotoxicity on breast cancer by stabilizing the BP activity and offering endocytic pathways. Additionally, BP and LPPC-encapsulated BP induced cell cycle arrest at the G0/G1 phase and might trigger both extrinsic as well as intrinsic cell apoptosis pathway, resulting in cell death. Moreover, the BP/LPPC complex had a synergistic effect with doxorubicin of enhancing the inhibitory effect on breast cancer cells. Consequently, LPPC-encapsulated BP could improve the anti-cancer effects on breast cancer in vitro. In conclusion, BP exhibited an anti-cancer effect on breast cancer cells, and LPPC encapsulation efficiently improved the cytotoxicity of BP via an acceleration of entrapment efficiency to induce cell cycle block and apoptosis. Furthermore, BP/LPPC exhibited a synergistic effect in combination with doxorubicin.
Keywords: Polycationic liposome containing PEI and polyethylene glycol complex (LPPC), n-Butylidenephthalide (BP), Cell apoptosis, Cell cycle, Synergistic effect

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact