3.2
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1449-1907
Int J Med Sci 2021; 18(13):2920-2929. doi:10.7150/ijms.61191 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Selective brain cooling achieves peripheral organs protection in hemorrhagic shock resuscitation via preserving the integrity of the brain-gut axis
1. Department of Intensive Care Medicine, Chi Mei Medical Center, Liouying, Tainan, Taiwan.
2. Department of Nursing, Min-Hwei College of Health Care Management, Tainan, Taiwan.
3. Department of Emergency Medicine, Chi Mei Medical Center, Tainan, Taiwan
4. Department of Senior Services, Southern Taiwan University of Science and Technology, Tainan, Taiwan.
5. Department of Environmental and Occupational Health, College of Medicine, National Cheng Kung University, Tainan, Taiwan.
6. Department of Medical Research, Chi Mei Medical Center, Tainan, Taiwan
7. Department of Medicine, Taipei Medical University, Taipei, Taiwan.
8. Division of Neurosurgery, Department of Surgery, Chi Mei Medical Center, Tainan, Taiwan.
Abstract
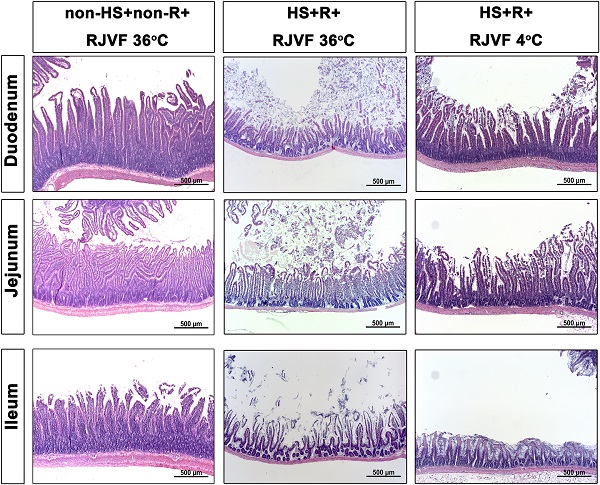
Background: Although whole-body cooling has been reported to improve the ischemic/reperfusion injury in hemorrhagic shock (HS) resuscitation, it is limited by its adverse reactions following therapeutic hypothermia. HS affects the experimental and clinical bowel disorders via activation of the brain-gut axis. It is unknown whether selective brain cooling achieves beneficial effects in HS resuscitation via preserving the integrity of the brain-gut axis.
Methods: Male Sprague-Dawley rats were bled to hypovolemic HS and resuscitated with blood transfusion followed by retrograde jugular vein flush (RJVF) with 4 °C or 36 °C normal saline. The mean arterial blood pressure, cerebral blood flow, and brain and core temperature were measured. The integrity of intestinal tight junction proteins and permeability, blood pro-inflammatory cytokines, and multiple organs damage score were determined.
Results: Following blood transfusion resuscitation, HS rats displayed gut barrier disruption, increased blood levels of pro-inflammatory cytokines, and peripheral vital organ injuries. Intrajugular-based infusion cooled the brain robustly with a minimal effect on body temperature. This brain cooling significantly reduced the HS resuscitation-induced gut disruption, systemic inflammation, and peripheral vital organ injuries in rats.
Conclusion: Resuscitation with selective brain cooling achieves peripheral vital organs protection in hemorrhagic shock resuscitation via preserving the integrity of the brain-gut axis.
Keywords: hemorrhagic shock, resuscitation, gut barrier, selective brain cooling

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact