ISSN: 1449-1907
Int J Med Sci 2021; 18(13):2905-2909. doi:10.7150/ijms.57010 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Association of QRS-T angle and Late Gadolinium Enhancement in patients with a Clinical Suspicion of Myocarditis
1. Department of Cardiology and Angiology, Contilia Heart and Vascular Center, Elisabeth-Krankenhaus Essen, Essen, Germany.
2. Ruhr University Bochum, Bochum, Germany.
3. Department of Diagnostic and Interventional Radiology and Neuroradiology, University Hospital Essen, Essen, Germany.
Abstract
Objective: To investigate the association of a wide QRS-T angle on the surface ECG and late gadolinium enhancement on contrast-enhanced cardiovascular magnetic (CMR) imaging in patients with clinically suspected myocarditis.
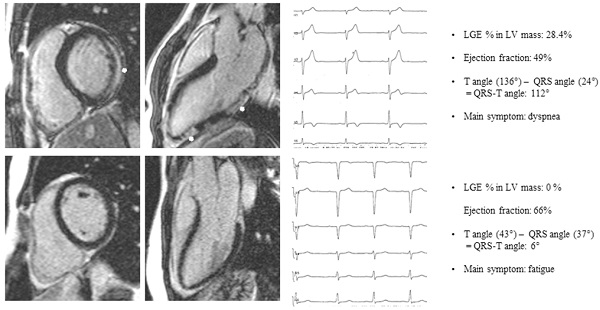
Background: Diagnosis and risk stratification in patients with suspected myocarditis is particularly challenging due to a great spectrum of clinical presentations. Late gadolinium enhancement (LGE) visualizes myocardial necrosis and fibrosis in patients with biopsy-proven myocarditis. The presence or absence of late gadolinium enhancements in these patients is prognostically meaningful. The QRS-T angle from the surface ECG, on the other hand, may serve as a simple and easily available risk marker in suspected myocarditis.
Methods: We enrolled 97 consecutive patients that were referred to CMR imaging for a clinical suspicion of myocarditis. All patients obtained a standardized digital 12-lead ECG for the calculation of the QRS-T angle and underwent contrast-enhanced CMR imaging. Patients were divided into two groups according to the absence or presence of LGE on CMR.
Results: 78 of 97 patients with suspected myocarditis had LGE on CMR. Patients with LGE had wider QRS-T angles as compared to the patient group without LGE (53.95-47.5 vs. 26.2-21.2; p<0.001). The sensivity, specificity, negative predictive value and positive predictive value for a QRS-T angle above 90 degrees for LGE positive myocarditis were 16.5%, 100%, 24.7%, and 100%, respectively.
Conclusion: A wide QRS-T angle of 90 degrees or more is linked to myocardial fibrosis or necrosis (late gadolinium enhancement) in patients with suspected myocarditis.
Keywords: QRS-T angle, cardiovascular magnetic resonance, late gadolinium enhancement, fibrosis, necrosis, myocarditis

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact