3.2
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1449-1907
Int J Med Sci 2021; 18(13):2897-2904. doi:10.7150/ijms.44801 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Evaluation of atherogenic lipoprotein-cholesterol to HDL cholesterol ratio as a prognostic test for ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction
1. Department of Laboratory Medicine, Shanghai General Hospital, Shanghai Jiao Tong University School of Medicine, Shanghai, China.
2. Clinical Laboratory Medicine Center, Shanghai Children's Hospital, Shanghai, China.
3. Department of Cardiology, Shanghai Ninth people's Hospital, Shanghai Jiao Tong University School of Medicine, Shanghai, China.
4. Department of Cardiology, Shanghai General Hospital, Shanghai Jiao Tong University School of Medicine, Shanghai, China.
5. Department of Laboratory Medicine, Shanghai General Hospital Jiading Branch, Shanghai, China.
#These authors contributed equally to this work.
Abstract
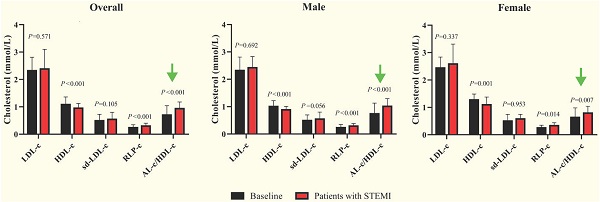
Background: The detectable component of triglyceride-rich lipoproteins (TGRLs), remnant lipoprotein cholesterol (RLP-c), has been proven being correlated with the progression of atherosclerosis and myocardial infarction. However, when taken as a risk predictor, the prognostic and diagnostic potential of RLP-c remains controversial in studies. In this study, we evaluated the hypothesis that atherogenic lipoprotein-cholesterol (AL-c), representing the sum of RLP-c and the sd-LDL-c, to the HDL-c ratio, could represent a better predictive indicator than RLP-c alone in ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI).
Methods: The 316 consecutive patients suffering from persistent chest discomfort admitted to the Shanghai General Hospital between January 2018 and June 2018 were enrolled. 149 STEMI patients (62% men, mean age 69.6 ± 13.3 years) were included as the study cohort. The AL-c/HDL-c ratio was calculated on admission in a cohort of electrocardiogram-confirmed STEMI patients and compared to other lipid profiles as a predictive indicator.
Results: The AL-c/HDL-c ratio was significantly increased in STEMI patients compared with apparently healthy adults (0.93; IQR [0.71-1.18] vs 0.70; IQR [0.45-1.04]; p < 0.001). Gender dependency existed, and the male and female patients had median AL-c/HDL-c ratios of 1.01 and 0.79, respectively (p < 0.001). Compared to RLP-c, the AL-c/HDL-c ratio had a better prognostic value to predict STEMI risk in both sexes (AUC of 0.672 with a sensitivity of 0.794 in males and 0.613 with a sensitivity of 0.684 in females).
Conclusions: The AL-c/HDL-c ratio could represent a convenient and sensitive biomarker for screening and predicting STEMI risk.
Keywords: remnant lipoprotein cholesterol, atherogenic lipoprotein, STEMI

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact