ISSN: 1449-1907
Int J Med Sci 2021; 18(11):2366-2371. doi:10.7150/ijms.49337 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Clinical course of patients on maintenance hemodialysis and COVID-19: a retrospective longitudinal study
1. Department of Nephrology, Union Hosptial, Tongji Medical College, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan 430033, Hubei, China.
2. Department of Surgery, Tongji Hosptial, Tongji Medical College, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan 430030, Hubei, China.
3. Department and Institute of Urology, Tongji Hosptial, Tongji Medical College, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan 430030, Hubei, China.
4. Tongji multidisciplinary Team for Treating COVID-19 (TTTC), Tongji Hosptial, Tongji Medical College, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan 430030, Hubei, China.
Abstract
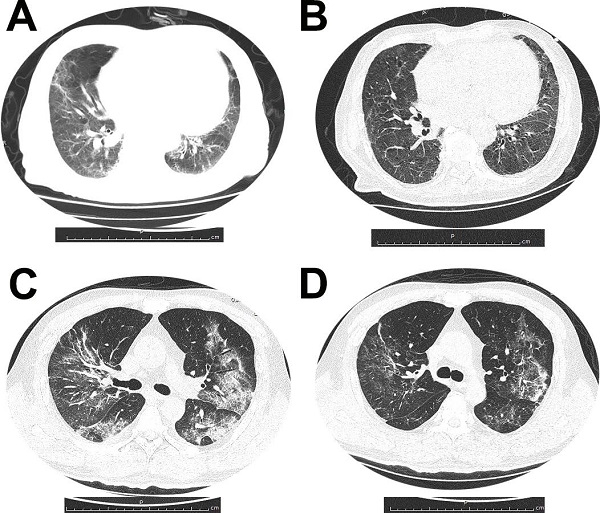
Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) emerges as a global pandemic and there is a lack of evidence about the clinical course and outcome of patients on maintenance hemodialysis (MHD). Here we conducted a retrospective longitudinal study aimed to analyze the clinical features and outcome of MHD patients hospitalized with COVID-19. Of 3126 inpatients with COVID-19 at 3 Branches of Wuhan Tongji Hospital from Jan 18th to Mar 9th, 2020, 19 patients were undergoing maintenance hemodialysis. Among the 19 MHD patients with COVID-19, 6 patients (31.6%) died, and 13 patients (68.4%) were able to be discharged. Baseline characteristics, clinical courses, laboratory findings, and dynamic trajectories of major laboratory markers were compared between survivors and nonsurvivors. According to our findings, MHD patients with COVID-19 who experienced non-surviving outcome had more elevated CRP, IL6 and procalcitonin as well as fibrinogen levels at various points compared to survivors. Thus the dysregulation of immune response as well as coagulation abnormalities might be highly involved in the pathological process of COVID-19, contributing to the poor prognosis in MHD patients.
Keywords: maintenance hemodialysis patients, COVID-19, clinical features, outcome, SARS-COV-2

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact