3.2
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1449-1907
Int J Med Sci 2021; 18(10):2176-2186. doi:10.7150/ijms.56564 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Effect of 5-azacytidine (5-aza) on UCP2 expression in human liver and colon cancer cells
1. College of Veterinary Medicine & Institute of Veterinary Science, Kangwon National University, Chuncheon 24341, Korea.
2. College of Animal Life Sciences, Kangwon National University, Chuncheon 24341, Korea.
3. Faculty of Veterinary Medicine, Hokkaido University, Sapporo, Japan.
Abstract
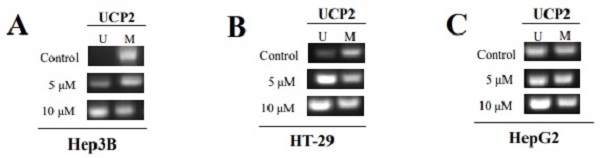
The function of the uncoupling protein 2 (UCP2) is different for each cancer cell. However, the mechanism of expression is still unclear. DNA methylation affects protein expression and is one factor that transforms normal cells into cancer cells. In this study, the hepatocellular carcinoma Hep3B and HepG2 cells and colorectal cancer HT-29 cells were treated with 5-azacytidine (5-aza), a DNA demethylation agent, to observe the modification of UCP2 expression and the methylation degree in the UCP2 promoter region. Promoter basal activity and degree of UCP2 expression were measured in Hep3B, HepG2, and HT-29 cells. In addition, methylation-specific PCR (MSP) was performed to investigate the degree of methylation in the UCP2 promoter region. The methylation region in the UCP2 promoter was confirmed based on bisulfite sequencing. In Hep3B cells in which UCP2 mRNA was not transcribed, the promoter basal activity was significantly higher than in HT-29 or HepG2 cells in which UCP2 mRNA was transcribed. Treatment with 5-aza increased UCP2 expression in Hep3B and HT-29 cells; however, the expression in HepG2 cells was unchanged. The UCP2 promoter in Hep3B cells has numerous methylated regions compared with HT-29 and HepG2 cells. The results of the present study revealed that inhibition of UCP2 expression in Hep3B cells was due to methylation of the promoter region. Investigating the mechanism that induces UCP2 expression in cancer cells is important to understand the function of UCP2, which could aid in cancer treatment.
Keywords: 5-azacytidine, bisulfite sequencing, DNA methylation, methylation-specific PCR (MSP), UCP2, UCP2 promoter active.

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact