3.2
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1449-1907
Int J Med Sci 2021; 18(10):2128-2136. doi:10.7150/ijms.48614 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Chest CT Imaging Features of Typical Covert COVID-19 Cases
1. Department of Radiology, Union Hospital, Tongji Medical College, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan 430022, China.
2. Hubei Province Key Laboratory of Molecular Imaging, Wuhan 430022, China.
3. Department of Orthopaedics, Union Hospital, Tongji Medical College, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan 430022, China.
4. MSC Clinical & Technical Solutions, Philips Healthcare, Beijing 100000, China.
5. Department of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine, Union Hospital, Tongji Medical College, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan 430022, China.
6. Hayward Genetics Center, Tulane University School of Medicine, New Orleans, Louisiana, USA.
* Meng Dai and Liu Ouyang contributed equally to this work.
Abstract
Purpose: To analyze the chest CT imaging findings of patients with initial negative RT-PCR and to compare with the CT findings of the same sets of patients when the RT-PCR turned positive for SARS-CoV-2 a few days later.
Materials and methods: A total of 32 patients (8 males and 24 females; 52.9±7years old) with COVID-19 from 27 January and 26 February 2020 were enrolled in this retrospective study. Clinical and radiological characteristics were analyzed.
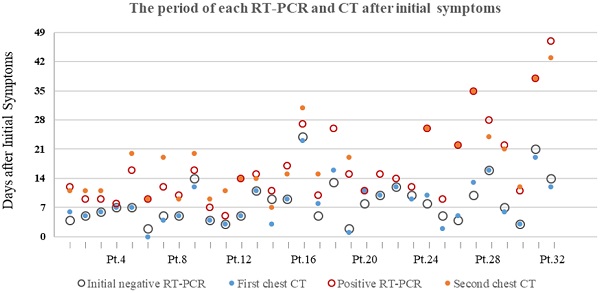
Results: The median period (25%, 75%) between initial symptoms and the first chest CT, the initial negative RT-PCR, the second CT and the positive RT-PCR were 7(4.25,11.75), 7(5,10.75), 15(11,23) and 14(10,22) days, respectively. Ground glass opacities was the most frequent CT findings at both the first and second CTs. Consolidation was more frequently observed on lower lobes, and more frequently detected during the second CT (64.0%) with positive RT-PCR than the first CT with initial negative RT-PCR (53.1%). The median of total lung severity score and the number of lobes affected had significant difference between twice chest CT (P=0.007 and P=0.011, respectively).
Conclusion: In the first week of disease course, CT was sensitive to the COVID-19 with initial negative RT-PCR. Throat swab test turned positive while chest CT mostly demonstrated progression.
Keywords: RT-PCR, GGO, COVID-19, CT, covert coronavirus infections.

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact