ISSN: 1449-1907
Int J Med Sci 2021; 18(8):1848-1856. doi:10.7150/ijms.55866 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Bitter Melon Extract Yields Multiple Effects on Intestinal Epithelial Cells and Likely Contributes to Anti-diabetic Functions
1. Department of Biological Science and Technology, National Pingtung University of Science and Technology, Pingtung 91201, Taiwan.
2. Department of Life Sciences, National University of Kaohsiung, Kaohsiung 811, Taiwan.
3. Department of Agroindustrial Biotechnology, Brawijaya University, Jalan, Veteran Malang 65145, Indonesia.
4. Department of English, National Kaohsiung Normal University, Kaohsiung 80201, Taiwan.
* These authors contributed to this work equally.
Abstract
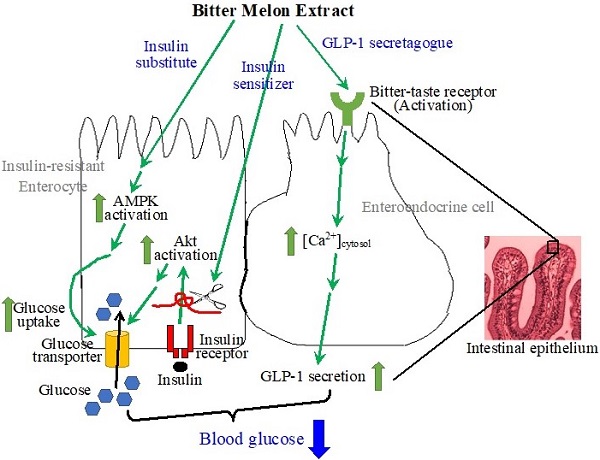
The intestines have been recognized as important tissues for metabolic regulation, including glycemic control, but their vital role in promoting the anti-diabetic effects of bitter melon, the fruit of Momordica charantia L, has seldom been characterized, nor acknowledged. Evidence suggests that bitter melon constituents can have substantial interactions with the intestinal epithelial cells before circulating to other tissues. We therefore characterized the effects of bitter melon extract (BME) on intestinal epithelial cells. BME was found to contain substantial amounts of carbohydrates, proteins, and triterpenoids. TNF-α induced insulin resistance in an enterocyte cell line of IEC-18 cells, and BME promoted glucose utilization of the insulin-resistant cells. Further analysis suggested that the increased glucose consumption was a result of the combined effects of insulin sensitizing and insulin substitution functions of BME. The functions of insulin substitution were likely generated due to the activation of AMP-activated protein kinase. Meanwhile, BME acted as a glucagon-like peptide 1 (GLP-1) secretagogue on enteroendocrine cells, which may be mediated by the activation of bitter-taste receptors. Therefore, BME possesses insulin sensitizing, insulin substitution, and GLP-1 secretagogue functions upon intestinal cells. These effects of BME on intestinal cells likely play a significant part in the anti-diabetic action of bitter melon.
Keywords: AMP-activated protein kinase, bitter-taste receptor, glucagon-like peptide 1, diabetes, intestine, Momordica charantia.

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact