ISSN: 1449-1907
Int J Med Sci 2021; 18(6):1474-1483. doi:10.7150/ijms.53641 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Cardiac Troponin I association with critical illness and death risk in 726 seriously ill COVID-19 patients: A retrospective cohort study
1. Department and Institute of Infectious Disease, Tongji Hospital, Tongji Medical College, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan 430030, China.
2. Department of Microbiology and Infectious Disease Center, School of Basic Medical Sciences, Peking University, Beijing 100191, China.
3. MHC Key Laboratory of Biosafety, National Institute for Viral Disease Control and Prevention, China CDC, Beijing 102206, China.
#These authors contributed equally to the manuscript.
Abstract
Background: For coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19), early identification of patients with serious symptoms at risk of critical illness and death is important for personalized treatment and balancing medical resources.
Methods: Demographics, clinical characteristics, and laboratory tests data from 726 patients with serious COVID-19 at Tongji Hospital (Wuhan, China) were analyzed. Patients were classified into critical group (n = 174) and severe group (n= 552), the critical group was sub-divided into survivors (n = 47) and non-survivors (n = 127).
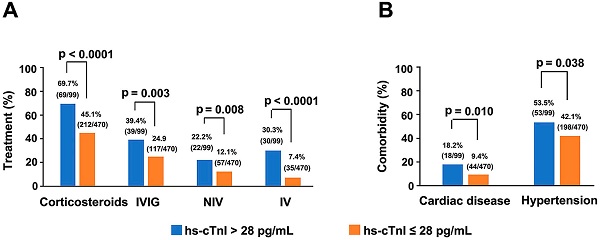
Results: Multivariable analyses revealed the risk factors associated with critical illness in serious patients were: Advanced age, high respiratory rate (RR), high lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) level, high hypersensitive cardiac troponin I (hs-cTnI) level, and thrombocytopenia on admission. High hs-cTnI level was the independent risk factor of mortality among critically ill patients in the unadjusted and adjusted models. ROC curves demonstrated that hs-cTnI and LDH were predictive factors for critical illness in patients with serious COVID-19 whereas procalcitonin and D-Dimer with hs-cTnI and LDH were predictive parameters in mortality risk.
Conclusions: Advanced age, high RR, LDH, hs-cTnI, and thrombocytopenia, constitute risk factors for critical illness among patients with serious COVID-19, and the hs-cTnI level helps predict fatal outcomes in critically ill patients.
Keywords: Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19), severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus (SARS-CoV-2), prognosis, hypersensitive cardiac troponin I (hs-cTnI), lactate dehydrogenase (LDH)

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact