3.2
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1449-1907
Int J Med Sci 2021; 18(6):1449-1455. doi:10.7150/ijms.51117 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Elevated Creatinine Clearance in Lupus Nephritis patients with Normal Creatinine
Department of Rheumatology, Qilu Hospital of Shandong University, Ji'nan 250012, Shandong, China.
#These authors contributed equally to this work.
Abstract
Objectives: The present study aimed to observe the differences in creatinine clearance (Ccr) in systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) patients with normal serum creatinine at different levels of urinary protein.
Method: The present cross-sectional study included 177 SLE patients with normal serum creatinine from Qilu Hospital of Shandong University between January 2010 and April 2020. The following data were collected: blood urea nitrogen (BUN), serum creatinine (Cr), serum total protein, serum albumin, immunoglobulin (Ig) G, IgA, IgM, complement 3, complement 4, anti-ds-DNA antibody, routine urine test, urine protein/creatinine ratio (UPCR) (g/g), and the SLE disease activity index. The estimated Ccr was calculated according to the Cockcroft formula.
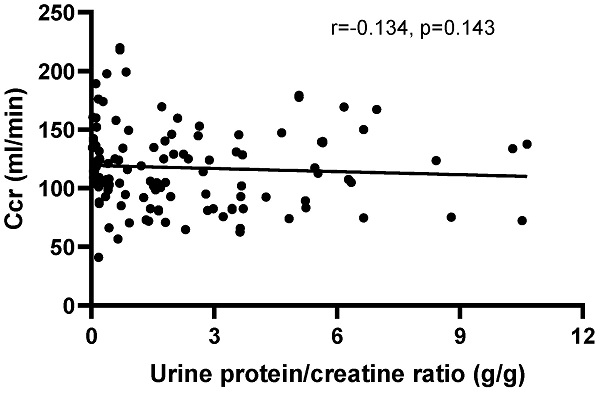
Results: 123 patients were with positive urinary protein (Lupus Nephritis, LN group) and 54 patients were with negative urinary protein (Non-LN group). Compared with the Non-LN group, the LN group had higher BUN (5.76±3.22 vs. 4.78±1.58, P=0.007) and Cr (62.36±19.53 vs. 54.83±11.09, P=0.001). There was a strong correlation between the UPCR and the semi-quantitative determination of urine protein in LN patients (r=0.9583, P=0.0417). The serum creatinine levels were significantly higher in patients with urine protein 3+ (72.97±25.16) or massive proteinuria (62.32±19.66) than the other groups. Patients with urinary protein ± exhibited a significantly elevated Ccr when compared to patients with urinary protein 3+ (130.6±44.15 vs. 110.5±33.50, P=0.02), and patients with UPCR<0.15 g/g had higher Ccr than other groups and showed significantly increased Ccr compared with patients with UPCR≥0.15 g/g (132.44±21.02 vs. 115.14±35.89, P=0.007).
Conclusions: Early renal function impairment may be present in LN patients. The kidneys of LN patients with urinary protein ± or UPCR<0.15 g/g are in a state of hyperfunction.
Keywords: lupus nephritis, creatinine, creatinine clearance, protein urine, urine protein/creatinine ratio

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact