ISSN: 1449-1907
Int J Med Sci 2021; 18(6):1442-1448. doi:10.7150/ijms.43167 This issue Cite
Research Paper
ATF4 promotes lung cancer cell proliferation and invasion partially through regulating Wnt/β-catenin signaling
1. Department of Pathology, First affiliated hospital and College of Basic Medical Sciences of China Medical University, 110001, Shenyang, China.
2. Department of Breast Surgery, Department of Surgical Oncology, Research Unit of General Surgery, the First Affiliated Hospital of China Medical University, 110001, Shenyang, China.
Abstract
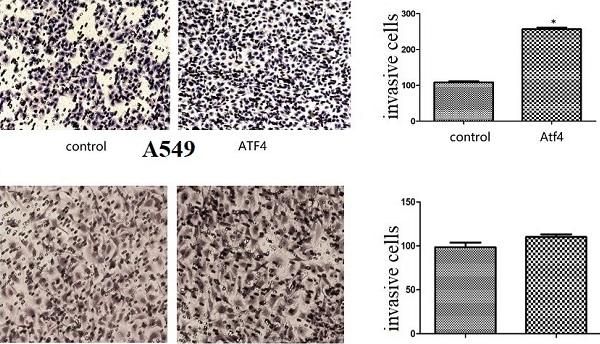
Activating transcription factor 4 (ATF4) is a member of the cAMP response element binding (CREB) protein family and has been reported to participate in cancer progression; however, its molecular mechanism is not fully understood. In this study, we investigated the function of ATF4 in non-small cell lung cancer and its molecular regulation. We detected cytoplasmic and nuclear ATF4 expression in lung cancer A549, H1299, and LK2 cells, and the total expression of ATF4 was higher than that in HBE cells (p < 0.05). Higher nuclear ATF4 expression was detected in all these cells compared to cytoplasmic ATF4 expression (p < 0.05). Overexpression of ATF4 in A549 cells significantly promoted cancer cell growth and invasion (p < 0.05). Expression of Wnt signaling molecules, including β-catenin, MMP7, and cyclin D1, and the activity of canonical Wnt signaling were also significantly promoted by ATF4 (p < 0.05). ICG001, a canonical Wnt signaling inhibitor that selectively inhibits β-catenin/ cyclic adenosine monophosphate response element binding protein (CBP) interaction, significantly inhibited cancer cell invasion and Wnt signaling. The function of ATF4 was also significantly inhibited by ICG001 (p < 0.05). However, compared to treatment with ICG001, the invasion ability of cancer cells treated with both ICG001 and ATF4 cDNA significantly increased (p < 0.05), which indicates that the function of ATF4 was not dependent only on Wnt/β-catenin signaling. The function of ATF4 in the regulation of β-catenin expression was not significantly affected by ICG001 (p > 0.05). The function of ATF4 to promote the activity of Wnt/β-catenin signaling in cancer cells was abolished by treatment with ICG001 (p > 0.05). These results indicate that ATF4 may contribute to lung cancer progression at least partly by regulating Wnt/β-catenin signaling.
Keywords: ATF4, β-catenin, lung cancer, proliferation, invasion

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact